A critical role of the adenosine A2A receptor in extrastriatal neurons in modulating psychomotor activity as revealed by opposite phenotypes of striatum and forebrain A2A receptor knock-outs
- PMID: 18354001
- PMCID: PMC6670718
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5255-07.2008
A critical role of the adenosine A2A receptor in extrastriatal neurons in modulating psychomotor activity as revealed by opposite phenotypes of striatum and forebrain A2A receptor knock-outs
Abstract
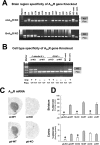
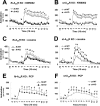
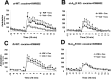
The function of striatal adenosine A(2A) receptors (A(2A)Rs) is well recognized because of their high expression levels and the documented antagonistic interaction between A(2A)Rs and dopamine D(2) receptors in the striatum. However, the role of extrastriatal A(2A)Rs in modulating psychomotor activity is largely unexplored because of the low level of expression and lack of tools to distinguish A(2A)Rs in intrinsic striatal versus nonstriatal neurons. Here, we provided direct evidence for the critical role of A(2A)Rs in extrastriatal neurons in modulating psychomotor behavior using newly developed striatum-specific A(2A)R knock-out (st-A(2A)R KO) mice in comparison with forebrain-specific A(2A)R KO (fb-A(2A)R KO) mice. In contrast to fb-A(2A)R KO (deleting A(2A)Rs in the neurons of striatum as well as cerebral cortex and hippocampus), st-A(2A)R KO mice exhibited Cre-mediated selective deletion of the A(2A)R gene, mRNA, and proteins in the neurons (but not astrocytes and microglial cells) of the striatum only. Strikingly, cocaine- and phencyclidine-induced psychomotor activities were enhanced in st-A(2A)R KO but attenuated in fb-A(2A)R KO mice. Furthermore, selective inactivation of the A(2A)Rs in extrastriatal cells by administering the A(2A)R antagonist KW6002 into st-A(2A)R KO mice attenuated cocaine effects, whereas KW6002 administration into wild-type mice enhanced cocaine effects. These results identify a critical role of A(2A)Rs in extrastriatal neurons in providing a prominent excitatory effect on psychomotor activity. These results indicate that A(2A)Rs in striatal and extrastriatal neurons exert an opposing modulation of psychostimulant effects and provide the first direct demonstration of a predominant facilitatory role of extrastriatal A(2A)Rs.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulation of fear responses by striatal and extrastriatal adenosine A2A receptors in forebrain.Biol Psychiatry. 2014 Jun 1;75(11):855-63. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2013.05.003. Epub 2013 Jun 29. Biol Psychiatry. 2014. PMID: 23820821 Free PMC article.
-
Adenosine A2A receptor antagonists exert motor and neuroprotective effects by distinct cellular mechanisms.Ann Neurol. 2008 Mar;63(3):338-46. doi: 10.1002/ana.21313. Ann Neurol. 2008. PMID: 18300283
-
Adenosine A₂A receptors in striatal glutamatergic terminals and GABAergic neurons oppositely modulate psychostimulant action and DARPP-32 phosphorylation.PLoS One. 2013 Nov 28;8(11):e80902. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0080902. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24312250 Free PMC article.
-
Anatomy of adenosine A2A receptors in brain: morphological substrates for integration of striatal function.Neurology. 2003 Dec 9;61(11 Suppl 6):S12-8. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000095205.33940.99. Neurology. 2003. PMID: 14663003 Review.
-
Progress in pursuit of therapeutic A2A antagonists: the adenosine A2A receptor selective antagonist KW6002: research and development toward a novel nondopaminergic therapy for Parkinson's disease.Neurology. 2003 Dec 9;61(11 Suppl 6):S97-100. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000095219.22086.31. Neurology. 2003. PMID: 14663020 Review.
Cited by
-
Optogenetic activation of intracellular adenosine A2A receptor signaling in the hippocampus is sufficient to trigger CREB phosphorylation and impair memory.Mol Psychiatry. 2015 Nov;20(11):1339-49. doi: 10.1038/mp.2014.182. Epub 2015 Feb 17. Mol Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 25687775 Free PMC article.
-
Adenosine A(2A) Receptors and A(2A) Receptor Heteromers as Key Players in Striatal Function.Front Neuroanat. 2011 Jun 17;5:36. doi: 10.3389/fnana.2011.00036. eCollection 2011. Front Neuroanat. 2011. PMID: 21731559 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of anti-inflammatory targets for Huntington's disease using a brain slice-based screening assay.Neurobiol Dis. 2011 Jul;43(1):248-56. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2011.03.017. Epub 2011 Mar 31. Neurobiol Dis. 2011. PMID: 21458569 Free PMC article.
-
40 Hz light flickering facilitates the glymphatic flow via adenosine signaling in mice.Cell Discov. 2024 Aug 6;10(1):81. doi: 10.1038/s41421-024-00701-z. Cell Discov. 2024. PMID: 39103336 Free PMC article.
-
Caffeine acts through neuronal adenosine A2A receptors to prevent mood and memory dysfunction triggered by chronic stress.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Jun 23;112(25):7833-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1423088112. Epub 2015 Jun 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26056314 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bastia E, Xu YH, Scibelli AC, Day YJ, Linden J, Chen JF, Schwarzschild MA. A crucial role for forebrain adenosine A(2A) receptors in amphetamine sensitization. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2005;30:891–900. - PubMed
-
- Benn CL, Farrell LA, Cha JH. Neurotransmitter receptor analysis in transgenic mouse models. Methods Mol Biol. 2004;277:231–260. - PubMed
-
- Chen JF, Beilstein M, Xu YH, Turner TJ, Moratalla R, Standaert DG, Aloyo VJ, Fink JS, Schwarzschild MA. Selective attenuation of psychostimulant-induced behavioral responses in mice lacking A(2A) adenosine receptors. Neuroscience. 2000;97:195–204. - PubMed
-
- Chen JF, Moratalla R, Yu L, Martin AB, Xu K, Bastia E, Hackett E, Alberti I, Schwarzschild MA. Inactivation of adenosine A2A receptors selectively attenuates amphetamine-induced behavioral sensitization. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2003;28:1086–1095. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
