Downregulation of the CB1 cannabinoid receptor and related molecular elements of the endocannabinoid system in epileptic human hippocampus
- PMID: 18354002
- PMCID: PMC6670708
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4465-07.2008
Downregulation of the CB1 cannabinoid receptor and related molecular elements of the endocannabinoid system in epileptic human hippocampus
Abstract
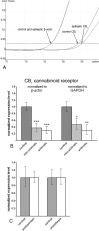
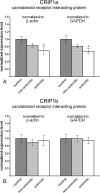
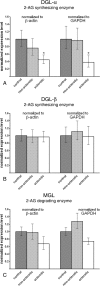
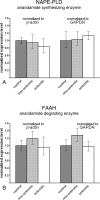
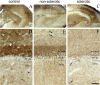
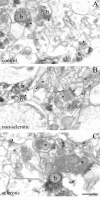
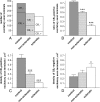
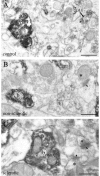
Endocannabinoid signaling is a key regulator of synaptic neurotransmission throughout the brain. Compelling evidence shows that its perturbation leads to development of epileptic seizures, thus indicating that endocannabinoids play an intrinsic protective role in suppressing pathologic neuronal excitability. To elucidate whether long-term reorganization of endocannabinoid signaling occurs in epileptic patients, we performed comparative expression profiling along with quantitative electron microscopic analysis in control (postmortem samples from subjects with no signs of neurological disorders) and epileptic (surgically removed from patients with intractable temporal lobe epilepsy) hippocampal tissue. Quantitative PCR measurements revealed that CB(1) cannabinoid receptor mRNA was downregulated to one-third of its control value in epileptic hippocampus. Likewise, the cannabinoid receptor-interacting protein-1a mRNA was decreased, whereas 1b isoform levels were unaltered. Expression of diacylglycerol lipase-alpha, an enzyme responsible for 2-arachidonoylglycerol synthesis, was also reduced by approximately 60%, whereas its related beta isoform levels were unchanged. Expression level of N-acyl-phosphatidylethanolamine-hydrolyzing phospholipase D and fatty acid amide hydrolase, metabolic enzymes of anandamide, and 2-arachidonoylglycerol's degrading enzyme monoacylglycerol lipase did not change. The density of CB(1) immunolabeling was also decreased in epileptic hippocampus, predominantly in the dentate gyrus, where quantitative electron microscopic analysis did not reveal changes in the ratio of CB(1)-positive GABAergic boutons, but uncovered robust reduction in the fraction of CB(1)-positive glutamatergic axon terminals. These findings show that a neuroprotective machinery involving endocannabinoids is impaired in epileptic human hippocampus and imply that downregulation of CB(1) receptors and related molecular components of the endocannabinoid system may facilitate the deleterious effects of increased network excitability.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Molecular reorganization of endocannabinoid signalling in Alzheimer's disease.Brain. 2011 Apr;134(Pt 4):1041-60. doi: 10.1093/brain/awr046. Brain. 2011. PMID: 21459826 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of the sites of 2-arachidonoylglycerol synthesis and action imply retrograde endocannabinoid signaling at both GABAergic and glutamatergic synapses in the ventral tegmental area.Neuropharmacology. 2008 Jan;54(1):95-107. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2007.05.028. Epub 2007 Jun 22. Neuropharmacology. 2008. PMID: 17655884 Free PMC article.
-
Alterations in the hippocampal endocannabinoid system in diet-induced obese mice.J Neurosci. 2010 May 5;30(18):6273-81. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2648-09.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20445053 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptic Reorganization of the Perisomatic Inhibitory Network in Hippocampi of Temporal Lobe Epileptic Patients.Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:7154295. doi: 10.1155/2017/7154295. Epub 2017 Jan 2. Biomed Res Int. 2017. PMID: 28116310 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The evolution and comparative neurobiology of endocannabinoid signalling.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2012 Dec 5;367(1607):3201-15. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2011.0394. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2012. PMID: 23108540 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Striatal CB1 and D2 receptors regulate expression of each other, CRIP1A and δ opioid systems.J Neurochem. 2013 Mar;124(6):808-20. doi: 10.1111/jnc.12139. Epub 2013 Jan 31. J Neurochem. 2013. PMID: 23286559 Free PMC article.
-
The GABAergic System and Endocannabinoids in Epilepsy and Seizures: What Can We Expect from Plant Oils?Molecules. 2022 Jun 4;27(11):3595. doi: 10.3390/molecules27113595. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35684543 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cannabinoids in the management of spasticity associated with multiple sclerosis.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2008 Oct;4(5):847-53. doi: 10.2147/ndt.s3208. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2008. PMID: 19183777 Free PMC article.
-
Fatty Acid Amides Synthesized from Andiroba Oil (Carapa guianensis Aublet.) Exhibit Anticonvulsant Action with Modulation on GABA-A Receptor in Mice: A Putative Therapeutic Option.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2020 Mar 10;13(3):43. doi: 10.3390/ph13030043. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32164340 Free PMC article.
-
CB2 cannabinoid receptors promote neural progenitor cell proliferation via mTORC1 signaling.J Biol Chem. 2012 Jan 6;287(2):1198-209. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.291294. Epub 2011 Nov 18. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22102284 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alger BE. Retrograde signaling in the regulation of synaptic transmission: focus on endocannabinoids. Prog Neurobiol. 2002;68:247–286. - PubMed
-
- Amaral DG. A Golgi study of cell types in the hilar region of the hippocampus in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1978;182:851–914. - PubMed
-
- Becker AJ, Chen J, Paus S, Normann S, Beck H, Elger CE, Wiestler OD, Blumcke I. Transcriptional profiling in human epilepsy: expression array and single cell real-time qRT-PCR analysis reveal distinct cellular gene regulation. NeuroReport. 2002;13:1327–1333. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
