BH3-only proteins Noxa, Bmf, and Bim are necessary for arsenic trioxide-induced cell death in myeloma
- PMID: 18354037
- PMCID: PMC2384139
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2007-10-116889
BH3-only proteins Noxa, Bmf, and Bim are necessary for arsenic trioxide-induced cell death in myeloma
Abstract
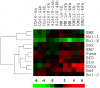
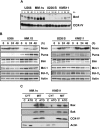
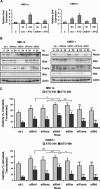
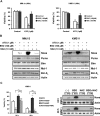
The use of arsenic trioxide (ATO) to treat multiple myeloma (MM) is supported by preclinical studies as well as several phase 2 studies, but the precise mechanism(s) of action of ATO has not been completely elucidated. We used gene expression profiling to determine the regulation of apoptosis-related genes by ATO in 4 MM cell lines and then focused on Bcl-2 family genes. ATO induced up-regulation of 3 proapoptotic BH3-only proteins (Noxa, Bmf, and Puma) and down-regulation of 2 antiapoptotic proteins Mcl-1 and Bcl-X(L). Coimmunoprecipitation demonstrated that Noxa and Puma bind Mcl-1 to release Bak and Bim within 6 hours of ATO addition. Bak and Bim are also released from Bcl-X(L). Silencing of Bmf, Noxa, and Bim significantly protected cells from ATO-induced apoptosis, while Puma silencing had no effect. Consistent with a role for Noxa inhibition of Mcl-1, the Bad-mimetic ABT-737 synergized with ATO in the killing of 2 MM lines. Finally, Noxa expression was enhanced by GSH depletion and inhibited by increasing GSH levels in the cells. Understanding the pattern of BH3-only protein response should aid in the rational design of arsenic-containing regimens.
Figures



References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, et al. Cancer statistics, 2006. CA Cancer J Clin. 2006;56:106–130. - PubMed
-
- Hideshima T, Leif Bergsagel P, Kuehl WM, Anderson KC. Advances in biology of multiple myeloma: clinical applications. Blood. 2004;104:607–618. - PubMed
-
- Rousselot P, Labaume S, Marolleau JP, et al. Arsenic trioxide and melarsoprol induce apoptosis in plasma cell lines and in plasma cells from myeloma patients. Cancer Res. 1999;59:1041–1048. - PubMed
-
- Park WH, Seol JG, Kim ES, et al. Arsenic trioxide-mediated growth inhibition in MC/CAR myeloma cells via cell cycle arrest in association with induction of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, p21, and apoptosis. Cancer Res. 2000;60:3065–3071. - PubMed
-
- Grad JM, Bahlis NJ, Reis I, Oshiro MM, Dalton WS, Boise LH. Ascorbic acid enhances arsenic trioxide-induced cytotoxicity in multiple myeloma cells. Blood. 2001;98:805–813. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

