AP214, an analogue of alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone, ameliorates sepsis-induced acute kidney injury and mortality
- PMID: 18354376
- PMCID: PMC2398767
- DOI: 10.1038/ki.2008.97
AP214, an analogue of alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone, ameliorates sepsis-induced acute kidney injury and mortality
Abstract
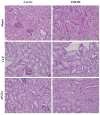
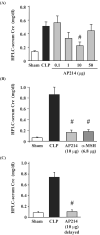
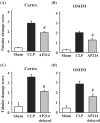
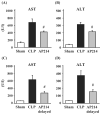
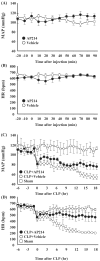
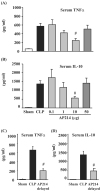
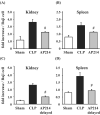
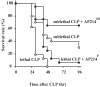
Sepsis remains a serious problem in critically ill patients with the mortality increasing to over half when there is attendant acute kidney injury. alpha-Melanocyte-stimulating hormone is a potent anti-inflammatory cytokine that inhibits many forms of inflammation including that with acute kidney injury. We tested whether a new alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone analogue (AP214), which has increased binding affinity to melanocortin receptors, improves sepsis-induced kidney injury and mortality using a cecal ligation and puncture mouse model. In the lethal cecal ligation-puncture model of sepsis, severe hypotension and bradycardia resulted and AP214 attenuated acute kidney injury of the lethal model with a bell-shaped dose-response curve. An optimum AP214 dose reduced acute kidney injury even when it was administered 6 h after surgery and it significantly improved blood pressure and heart rate. AP214 reduced serum TNF-alpha and IL-10 levels with a bell-shaped dose-response curve. Additionally; NF-kappaB activation in the kidney and spleen, and splenocyte apoptosis were decreased by the treatment. AP214 significantly improved survival in both lethal and sublethal models. We have shown that AP214 improves hemodynamic failure, acute kidney injury, mortality and splenocyte apoptosis attenuating pro- and anti-inflammatory actions due to sepsis.
Figures

References
-
- Martin GS, Mannino DM, Eaton S, et al. The epidemiology of sepsis in the United States from 1979 through 2000. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1546–1554. - PubMed
-
- Levy EM, Viscoli CM, Horwitz RI. The effect of acute renal failure on mortality. A cohort analysis. Jama. 1996;275:1489–1494. - PubMed
-
- Neveu H, Kleinknecht D, Brivet F, et al. Prognostic factors in acute renal failure due to sepsis. Results of a prospective multicentre study. The French Study Group on Acute Renal Failure. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1996;11:293–299. - PubMed
-
- Russell JA, Singer J, Bernard GR, et al. Changing pattern of organ dysfunction in early human sepsis is related to mortality. Crit Care Med. 2000;28:3405–3411. - PubMed
-
- Buras JA, Holzmann B, Sitkovsky M. Animal models of sepsis: setting the stage. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2005;4:854–865. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

