The closure of Pak1-dependent macropinosomes requires the phosphorylation of CtBP1/BARS
- PMID: 18354494
- PMCID: PMC2323256
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2008.59
The closure of Pak1-dependent macropinosomes requires the phosphorylation of CtBP1/BARS
Abstract
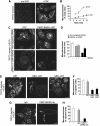
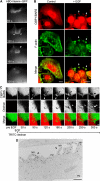
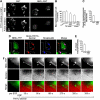
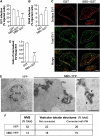
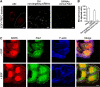
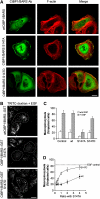
Membrane fission is an essential process in membrane trafficking and other cellular functions. While many fissioning and trafficking steps are mediated by the large GTPase dynamin, some fission events are dynamin independent and involve C-terminal-binding protein-1/brefeldinA-ADP ribosylated substrate (CtBP1/BARS). To gain an insight into the molecular mechanisms of CtBP1/BARS in fission, we have studied the role of this protein in macropinocytosis, a dynamin-independent endocytic pathway that can be synchronously activated by growth factors. Here, we show that upon activation of the epidermal growth factor receptor, CtBP1/BARS is (a) translocated to the macropinocytic cup and its surrounding membrane, (b) required for the fission of the macropinocytic cup and (c) phosphorylated on a specific serine that is a substrate for p21-activated kinase, with this phosphorylation being essential for the fission of the macropinocytic cup. Importantly, we also show that CtBP1/BARS is required for macropinocytic internalization and infection of echovirus 1. These results provide an insight into the molecular mechanisms of CtBP1/BARS activation in membrane fissioning, and extend the relevance of CtBP1/BARS-induced fission to human viral infection.
Figures
References
-
- Ahram M, Sameni M, Qiu RG, Linebaugh B, Kirn D, Sloane BF (2000) Rac1-induced endocytosis is associated with intracellular proteolysis during migration through a three-dimensional matrix. Exp Cell Res 260: 292–303 - PubMed
-
- Amyere M, Mettlen M, Van Der Smissen P, Platek A, Payrastre B, Veithen A, Courtoy PJ (2002) Origin, originality, functions, subversions and molecular signalling of macropinocytosis. Int J Med Microbiol 291: 487–494 - PubMed
-
- Barnes CJ, Vadlamudi RK, Mishra SK, Jacobson RH, Li F, Kumar R (2003) Functional inactivation of a transcriptional corepressor by a signaling kinase. Nat Struct Biol 10: 622–628 - PubMed
-
- Bonazzi M, Spano S, Turacchio G, Cericola C, Valente C, Colanzi A, Kweon HS, Hsu VW, Polishchuck EV, Polishchuck RS, Sallese M, Pulvirenti T, Corda D, Luini A (2005) CtBP3/BARS drives membrane fission in dynamin-independent transport pathways. Nat Cell Biol 7: 570–580 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

