The initiation factor eIF3-f is a major target for atrogin1/MAFbx function in skeletal muscle atrophy
- PMID: 18354498
- PMCID: PMC2367397
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2008.52
The initiation factor eIF3-f is a major target for atrogin1/MAFbx function in skeletal muscle atrophy
Abstract
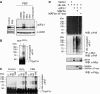
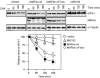
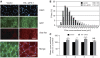
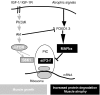
In response to cancer, AIDS, sepsis and other systemic diseases inducing muscle atrophy, the E3 ubiquitin ligase Atrogin1/MAFbx (MAFbx) is dramatically upregulated and this response is necessary for rapid atrophy. However, the precise function of MAFbx in muscle wasting has been questioned. Here, we present evidence that during muscle atrophy MAFbx targets the eukaryotic initiation factor 3 subunit 5 (eIF3-f) for ubiquitination and degradation by the proteasome. Ectopic expression of MAFbx in myotubes induces atrophy and degradation of eIF3-f. Conversely, blockade of MAFbx expression by small hairpin RNA interference prevents eIF3-f degradation in myotubes undergoing atrophy. Furthermore, genetic activation of eIF3-f is sufficient to cause hypertrophy and to block atrophy in myotubes, whereas genetic blockade of eIF3-f expression induces atrophy in myotubes. Finally, eIF3-f induces increasing expression of muscle structural proteins and hypertrophy in both myotubes and mouse skeletal muscle. We conclude that eIF3-f is a key target that accounts for MAFbx function during muscle atrophy and has a major role in skeletal muscle hypertrophy. Thus, eIF3-f seems to be an attractive therapeutic target.
Figures




References
-
- Asano K, Phan L, Anderson J, Hinnebusch AG (1998) Complex formation by all five homologues of mammalian translation initiation factor 3 subunits from yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem 27: 18573–18585 - PubMed
-
- Baar K, Esser K (1999) Phosphorylation of p70(S6k) correlates with increased skeletal muscle mass following resistance exercise. Am J Physiol 276: C120–C127 - PubMed
-
- Bodine SC, Latres E, Baumhueter S, Lai VK, Nunez L, Clarke BA, Poueymirou WT, Panaro FJ, Na E, Dharmarajan K, Pan ZQ, Valenzuela DM, DeChiara TM, Stitt TN, Yancopoulos GD, Glass DJ (2001a) Identification of ubiquitin ligases required for skeletal muscle atrophy. Science 294: 1704–1708 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

