Structures, folding patterns, and functions of intramolecular DNA G-quadruplexes found in eukaryotic promoter regions
- PMID: 18355457
- PMCID: PMC2585383
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biochi.2008.02.020
Structures, folding patterns, and functions of intramolecular DNA G-quadruplexes found in eukaryotic promoter regions
Abstract
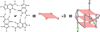
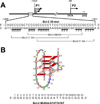
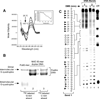
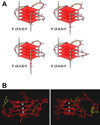
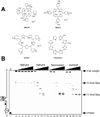
In its simplest form, a DNA G-quadruplex is a four-stranded DNA structure that is composed of stacked guanine tetrads. G-quadruplex-forming sequences have been identified in eukaryotic telomeres, as well as in non-telomeric genomic regions, such as gene promoters, recombination sites, and DNA tandem repeats. Of particular interest are the G-quadruplex structures that form in gene promoter regions, which have emerged as potential targets for anticancer drug development. Evidence for the formation of G-quadruplex structures in living cells continues to grow. In this review, we examine recent studies on intramolecular G-quadruplex structures that form in the promoter regions of some human genes in living cells and discuss the biological implications of these structures. The identification of G-quadruplex structures in promoter regions provides us with new insights into the fundamental aspects of G-quadruplex topology and DNA sequence-structure relationships. Progress in G-quadruplex structural studies and the validation of the biological role of these structures in cells will further encourage the development of small molecules that target these structures to specifically modulate gene transcription.
Figures

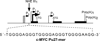
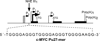
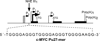











References
-
- Watson JD, Crick FHC. Molecular structure of nucleic acids: a structure for deoxyribose nucleic acid. Nature. 1953;171:737–738. - PubMed
-
- Wells RD. Unusual DNA structures. J Biol Chem. 1988;263:1095–1098. - PubMed
-
- Wells RD. Non-B DNA conformations, mutagenesis and disease. Trends Biochem Sci. 2007;32:271–278. - PubMed
-
- Raghavan SC, Lieber MR. DNA structure and human diseases. Front Biosci. 2007;12:4402–4408. - PubMed
-
- Bacolla A, Wells RD. Non-B DNA conformations, genomic rearrangements, and human disease. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:47411–47414. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

