Surfactant protein D alters allergic lung responses in mice and human subjects
- PMID: 18355911
- PMCID: PMC4145593
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaci.2008.02.011
Surfactant protein D alters allergic lung responses in mice and human subjects
Abstract
Background: Surfactant protein (SP) D has been proposed to be protective in allergic airway responses.
Objective: We aimed to determine the effect of SP-D deficiency on murine and human airway allergy.
Methods: Immunologic responses of SP-D gene-deficient mice (Sftpd-/-) at baseline and after 4 intranasal Aspergillus fumigatus exposures were assessed. In addition, the significance of a single nucleotide polymorphism (Met(11)Thr) in the human SP-D gene (known to decrease SP-D function) was investigated.
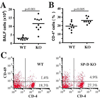
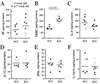
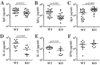
Results: Macrophage and neutrophil bronchoalveolar lavage fluid levels and large airway mucus production were increased in naive Sftpd-/- mice in association with increased lung CCL17 levels and CD4+ T cell numbers. T(H)2-associated antibody levels (IgG1 and IgE) were significantly lower in 4- to 5-week-old Sftpd-/- mice (P < .05). Accordingly, naive Sftpd-/- splenocytes released significantly less IL-4 and IL-13 on anti-CD3/CD28 stimulation (P < .01). After intranasal allergen exposures, a modest decrease in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid eosinophilia and IL-13 levels was observed in Sftpd-/- mice compared with values seen in wild-type mice in association with decreased airway resistance (P < .01). A single nucleotide polymorphism in the SFTPD gene, affecting SP-D levels and pathogen binding, was associated with decreased atopy in black subjects and potentially lower asthma susceptibility in white subjects.
Conclusion: Sftpd-/- mice have an impaired systemic T(H)2 response at baseline and reduced inflammation and airway responses after allergen exposure. Translational studies revealed that a polymorphism in the SFTPD gene was associated with lower atopy and possibly asthma susceptibility. Taken together, these results support the hypothesis that SP-D-dependent innate immunity influences atopy and asthma.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ozone Inhalation Attenuated the Effects of Budesonide on Aspergillus fumigatus-Induced Airway Inflammation and Hyperreactivity in Mice.Front Immunol. 2019 Sep 13;10:2173. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02173. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31572383 Free PMC article.
-
Surfactant protein D inhibits early airway response in Aspergillus fumigatus-sensitized mice.Clin Exp Allergy. 2006 Jul;36(7):930-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2006.02524.x. Clin Exp Allergy. 2006. PMID: 16839409
-
IL-4 and IL-13 form a negative feedback circuit with surfactant protein-D in the allergic airway response.J Immunol. 2006 Mar 15;176(6):3557-65. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.176.6.3557. J Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16517724
-
SP-D and regulation of the pulmonary innate immune system in allergic airway changes.Clin Exp Allergy. 2010 Apr;40(4):547-62. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2010.03483.x. Clin Exp Allergy. 2010. PMID: 20447075 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Linking surfactant protein SP-D and IL-13: implications in asthma and allergy.Mol Immunol. 2013 May;54(1):98-107. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2012.10.039. Epub 2012 Dec 7. Mol Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23220073 Review.
Cited by
-
Association of serum surfactant protein D and SFTPD gene variants with asthma in Danish children, adolescents, and young adults.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2022 Feb;10(2):189-200. doi: 10.1002/iid3.560. Epub 2021 Nov 15. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2022. PMID: 34780682 Free PMC article.
-
Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor is Essential in the Control of Lung Club Cell Homeostasis.J Inflamm Res. 2021 Feb 5;14:299-311. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S284800. eCollection 2021. J Inflamm Res. 2021. PMID: 33574691 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Association of Pulmonary Surfactant Protein Genes, SFTPA1, SFTPA2, SFTPB, SFTPC, and SFTPD With Cystic Fibrosis.Front Immunol. 2018 Oct 2;9:2256. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02256. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30333828 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic variants of SP-D confer susceptibility to radiation pneumonitis in lung cancer patients undergoing thoracic radiation therapy.Cancer Med. 2019 May;8(5):2599-2611. doi: 10.1002/cam4.2088. Epub 2019 Mar 21. Cancer Med. 2019. PMID: 30897289 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of surfactant protein D, interleukin-5, and eosinophilia on Cryptococcosis.Infect Immun. 2014 Feb;82(2):683-93. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00855-13. Epub 2013 Nov 25. Infect Immun. 2014. PMID: 24478083 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kishore U, Bernal AL, Kamran MF, Saxena S, Singh M, Sarma PU, et al. Surfactant proteins SP-A and SP-D in human health and disease. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 2005;53:399–417. - PubMed
-
- Wright JR. Immunoregulatory functions of surfactant proteins. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005;5:58–68. - PubMed
-
- Hohlfeld JM, Erpenbeck VJ, Krug N. Surfactant proteins SP-A and SP-D as modulators of the allergic inflammation in asthma. Pathobiology. 2002;70:287–292. - PubMed
-
- Haczku A. Role and regulation of lung collectins in allergic airway sensitization. Pharmacol Ther. 2005 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HL-076383/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HD43005-01/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL076383/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI042242/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI057803/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI42242/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL063329/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HD043005/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HL-63329/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AI057803/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 ES10957-03/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 ES010957/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

