Directly transmitted viral diseases: modeling the dynamics of transmission
- PMID: 18356058
- PMCID: PMC7127822
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tim.2008.01.007
Directly transmitted viral diseases: modeling the dynamics of transmission
Erratum in
- Trends Microbiol.2008 Jun;16(6):301
Abstract
A key hurdle in understanding the spread and control of infectious diseases is to capture appropriately the dynamics of pathogen transmission. As people and goods travel increasingly rapidly around the world, so do pathogens; we must be prepared to understand their spread, in terms of the contact network between hosts, viral life history and within-host dynamics. This will require collaborative work that takes into account viral life history, strategy and evolution, and host genetics, demographics and immunodynamics. Mathematical models are a useful tool for integrating the data and analyses from diverse fields that contribute to our understanding of viral transmission dynamics in heterogeneous host populations.
Figures
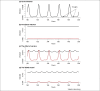
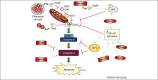
Similar articles
-
A Mathematical Framework for Predicting Lifestyles of Viral Pathogens.Bull Math Biol. 2020 Apr 29;82(5):54. doi: 10.1007/s11538-020-00730-1. Bull Math Biol. 2020. PMID: 32350621 Free PMC article.
-
[Interface between viruses and host].Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 2009 Jun;54(8 Suppl):899-900. Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 2009. PMID: 21089514 Japanese. No abstract available.
-
Cross-species virus transmission and the emergence of new epidemic diseases.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2008 Sep;72(3):457-70. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00004-08. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2008. PMID: 18772285 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How do viruses get around? A review of mathematical modeling of in-host viral transmission.Virology. 2025 Mar;604:110444. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2025.110444. Epub 2025 Jan 31. Virology. 2025. PMID: 39908773 Review.
-
ZOVER: the database of zoonotic and vector-borne viruses.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Jan 7;50(D1):D943-D949. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab862. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 34634795 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Testing the accuracy ratio of the Spatio-Temporal Epidemiological Modeler (STEM) through Ebola haemorrhagic fever outbreaks.Epidemiol Infect. 2016 May;144(7):1463-72. doi: 10.1017/S0950268815002939. Epidemiol Infect. 2016. PMID: 27029910 Free PMC article.
-
Association of host, agent and environment characteristics and the duration of incubation and symptomatic periods of norovirus gastroenteritis.Epidemiol Infect. 2015 Aug;143(11):2308-14. doi: 10.1017/S0950268814003288. Epub 2014 Dec 8. Epidemiol Infect. 2015. PMID: 25483148 Free PMC article.
-
Linked within-host and between-host models and data for infectious diseases: a systematic review.PeerJ. 2019 Jun 19;7:e7057. doi: 10.7717/peerj.7057. eCollection 2019. PeerJ. 2019. PMID: 31249734 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental Aspects of Cardiac Adaptation to Increased Workload.J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2023 May 10;10(5):205. doi: 10.3390/jcdd10050205. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2023. PMID: 37233172 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transboundary movements of foot-and-mouth disease from India to Sri Lanka: A common pattern is shared by serotypes O and C.PLoS One. 2019 Dec 31;14(12):e0227126. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0227126. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31891636 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Leo Y.S. Severe acute respiratory syndrome – Singapore, 2003. M.M.W.R. 2003;52:405–411. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

