Phosphorylation of MDMX mediated by Akt leads to stabilization and induces 14-3-3 binding
- PMID: 18356162
- PMCID: PMC2376244
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M710030200
Phosphorylation of MDMX mediated by Akt leads to stabilization and induces 14-3-3 binding
Abstract
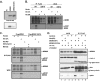
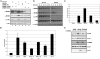
The critical tumor suppressor p53 is mutated or functionally inactivated in nearly all cancers. We have shown previously that the MDM2-MDMX complex functions as an integral unit in targeting p53 for degradation. Here we identify the small protein 14-3-3 as a binding partner of MDMX, which binds at the C terminus (Ser367) in a phosphorylation-dependent manner. Importantly, we demonstrate that the serine/threonine kinase Akt mediates phosphorylation of MDMX at Ser367. This phosphorylation leads to stabilization of MDMX and consequent stabilization of MDM2. Previous studies have shown that Akt phosphorylates and stabilizes MDM2. Our data suggest that stabilization of MDMX by Akt may be an alternative mechanism by which Akt up-regulates MDM2 protein levels and exerts its oncogenic effects on p53 in tumor cells.
Figures


References
-
- Vogelstein, B., Lane, D., and Levine, A. J. (2000) Nature 408 307–310 - PubMed
-
- Michael, D., and Oren, M. (2003) Semin. Cancer Biol. 13 49–58 - PubMed
-
- Finch, R. A., Donoviel, D. B., Potter, D., Shi, M., Fan, A., Freed, D. D., Wang, C. Y., Zambrowicz, B. P., Ramirez-Solis, R., Sands, A. T., and Zhang, N. (2002) Cancer Res. 62 3221–3225 - PubMed
-
- Parant, J., Chavez-Reyes, A., Little, N. A., Yan, W., Reinke, V., Jochemsen, A. G., and Lozano, G. (2001) Nat. Genet. 29 92–95 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

