Angiogenesis detected after embolic stroke in rat brain using magnetic resonance T2*WI
- PMID: 18356548
- PMCID: PMC2581408
- DOI: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.107.502146
Angiogenesis detected after embolic stroke in rat brain using magnetic resonance T2*WI
Abstract
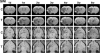
Background and purpose: This study uses T(2)* weighted imaging (T2*WI) to measure the temporal evolution of cerebral angiogenesis in rats subjected to embolic stroke up to 6 weeks after stroke onset with or without sildenafil treatment. Method- Male Wistar rats were subjected to embolic stroke and treated with saline (n=10) or with sildenafil (n=11), with treatment initiated at 24 hours and continued daily for 7 days after onset of ischemia. T2*WI measurements were performed at 24 hours after embolization and weekly up to 6 weeks using a 7-Tesla system. Histological measurements were obtained at 6 weeks after MRI scans.
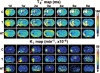
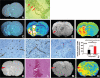
Results: Using T2*WI, cerebral angiogenesis was detected starting from 4 weeks and from 2 weeks after onset of embolic stroke in saline and sildenafil treated rats, respectively. Significant differences in the temporal and spatial features of angiogenesis after embolic stroke up to 6 weeks after onset of stroke were found between saline and sildenafil treated rats and were identified with T2*WI. MRI permeability parameter, K(i), complementarily detected angiogenesis after ischemia in embolic stroke rats. Sildenafil treatment of stroke rats significantly enhanced the angiogenesis, as confirmed histologically.
Conclusions: T2*WI can quantitatively measure the temporal evolution of angiogenesis in rats subjected to embolic stroke. Compared to control rats, sildenafil treatment significantly increased angiogenesis in treated animals up to 6 weeks after stroke.
Figures

References
-
- Ding G, Jiang Q, Zhang L, Zhang ZG, Knight RA, Soltanian-Zadeh H, Lu M, Ewing JR, Li Q, Whitton PA, Chopp M. Multiparametric ISODATA analysis of embolic stroke and rt-PA intervention in rat. J Neurol Sci. 2004;223:135–143. - PubMed
-
- Moseley ME, Cohen Y, Mintorovitch J, Chileuitt L, Shimizu H, Kucharczyk J, Wendland MF, Weinstein PR. Early detection of regional cerebral ischemia in cats: Comparison of diffusion- and T2-weighted MRI and spectroscopy. Magn Reson Med. 1990;14:330–346. - PubMed
-
- Hoehn-Berlage M, Eis M, Back T, Kohno K, Yamashita K. Changes of relaxation times (T1, T2) and apparent diffusion coefficient after permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion in the rat: temporal evolution, regional extent, and comparison with histology. Magn Reson Med. 1995;34:824–834. - PubMed
-
- Jiang Q, Zhang RL, Zhang ZG, Ewing JR, Divine GW, Chopp M. Diffusion-, T2-, and perfusion-weighted nuclear magnetic resonance imaging of middle cerebral artery embolic stroke and recombinant tissue plasminogen activator intervention in the rat. J Cereb Blood Flow and Metab. 1998;18:758–767. - PubMed
-
- Reichenbach JR, Venkatesan R, Schillinger DJ, Kido DK, Haacke ME. Small vessels in the human brain: MR venography with deoxyhemoglobin as an intrinsic contrast agent. Radiology. 1997;204:272–277. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P01 NS42345/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS048349/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS38292/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS038292/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL064766/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR019245/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS043324/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 NS042345/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 NS23393/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS43324/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS48349/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 NS023393/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 NS023393/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- HL64766/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS062832/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

