Repopulation of B-lymphocytes with restricted gene expression using haematopoietic stem cells engineered with lentiviral vectors
- PMID: 18356817
- PMCID: PMC2679983
- DOI: 10.1038/gt.2008.33
Repopulation of B-lymphocytes with restricted gene expression using haematopoietic stem cells engineered with lentiviral vectors
Abstract
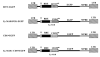
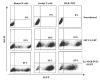
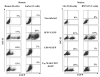
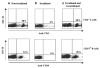
B-lymphocytes play a key role in the pathogenesis of many immune-mediated diseases, such as autoimmune and atopic diseases. Therefore, targeting B-lymphocytes provides a rationale for refining strategies to treat such diseases for long-term clinical benefits and minimal side effects. In this study we describe a protocol for repopulating irradiated mice with B-lymphocytes engineered for restricted expression of transgenes using haematopoietic stem cells. A self-inactivating lentiviral vector, which encodes enhanced green fluorescence protein (EGFP) from the spleen focus-forming virus (SFFV) promoter, was used to generate new vectors that permit restricted EGFP expression in B-lymphocytes. To achieve this, the SFFV promoter was replaced with the B-lymphocyte-restricted CD19 promoter. Further, an immunoglobulin heavy chain enhancer (Emu) flanked by the associated matrix attachment regions (MARs) was inserted upstream of the CD19 promoter. Incorporation of the Emu-MAR elements upstream of the CD19 promoter resulted in enhanced, stable and selective transgene expression in human and murine B-cell lines. In addition, this modification permitted enhanced selective EGFP expression in B-lymphocytes in vivo in irradiated mice repopulated with transduced bone marrow haematopoietic stem cells (BMHSCs). The study provides evidence for the feasibility of targeting B-lymphocytes for therapeutic restoration of normal B-lymphocyte functions in patients with B-cell-related diseases.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cell-specific and efficient expression in mouse and human B cells by a novel hybrid immunoglobulin promoter in a lentiviral vector.Gene Ther. 2007 Dec;14(23):1623-31. doi: 10.1038/sj.gt.3303021. Epub 2007 Sep 13. Gene Ther. 2007. PMID: 17851547
-
Lentivirus vectors incorporating the immunoglobulin heavy chain enhancer and matrix attachment regions provide position-independent expression in B lymphocytes.J Virol. 2003 Jul;77(13):7341-51. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.13.7341-7351.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12805432 Free PMC article.
-
Restriction of transgene expression to the B-lymphoid progeny of human lentivirally transduced CD34+ cells.Mol Ther. 2004 Jul;10(1):45-56. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2004.04.005. Mol Ther. 2004. PMID: 15233941
-
Transcriptional targeting of B cells with viral vectors.Eur J Cell Biol. 2012 Jan;91(1):86-96. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2011.01.016. Epub 2011 Mar 31. Eur J Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 21458103
-
Current landscape of vector safety and genotoxicity after hematopoietic stem or immune cell gene therapy.Leukemia. 2025 Jun;39(6):1325-1333. doi: 10.1038/s41375-025-02585-8. Epub 2025 Apr 8. Leukemia. 2025. PMID: 40200078 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Development of B-lineage predominant lentiviral vectors for use in genetic therapies for B cell disorders.Mol Ther. 2011 Mar;19(3):515-25. doi: 10.1038/mt.2010.259. Epub 2010 Dec 7. Mol Ther. 2011. PMID: 21139568 Free PMC article.
-
Different roles of G protein subunits beta1 and beta2 in neutrophil function revealed by gene expression silencing in primary mouse neutrophils.J Biol Chem. 2010 Aug 6;285(32):24805-14. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.142885. Epub 2010 Jun 4. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20525682 Free PMC article.
-
Lentiviral vectors for immune cells targeting.Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2010 Jun;32(2):208-18. doi: 10.3109/08923970903420582. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2010. PMID: 20085508 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Towards Physiologically and Tightly Regulated Vectored Antibody Therapies.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Apr 13;12(4):962. doi: 10.3390/cancers12040962. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32295072 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Incorporating double copies of a chromatin insulator into lentiviral vectors results in less viral integrants.BMC Biotechnol. 2009 Feb 24;9:13. doi: 10.1186/1472-6750-9-13. BMC Biotechnol. 2009. PMID: 19239708 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Browning JL. B cells move to centre stage: novel opportunities for autoimmune disease treatment. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006;5:564–576. - PubMed
-
- Cunningham-Rundles C, Ponda PP. Molecular defects in T- and B-cell primary immunodeficiency diseases. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005;11:880–892. - PubMed
-
- Mageed RA, Prud’homme GJ. Immunopathology and the gene therapy of lupus. Gene Therapy. 2003;10:861–874. - PubMed
-
- Youinou P, Jamin C, Pers JO, Berthou C, Saraux A, Renaudineau Y. B lymphocytes are required for development and treatment of autoimmune diseases. Ann NY Acad Sci. 2005;1050:19–33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

