Perioperative chemotherapy with FOLFOX4 and surgery versus surgery alone for resectable liver metastases from colorectal cancer (EORTC Intergroup trial 40983): a randomised controlled trial
- PMID: 18358928
- PMCID: PMC2277487
- DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60455-9
Perioperative chemotherapy with FOLFOX4 and surgery versus surgery alone for resectable liver metastases from colorectal cancer (EORTC Intergroup trial 40983): a randomised controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Surgical resection alone is regarded as the standard of care for patients with liver metastases from colorectal cancer, but relapse is common. We assessed the combination of perioperative chemotherapy and surgery compared with surgery alone for patients with initially resectable liver metastases from colorectal cancer.
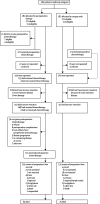
Methods: This parallel-group study reports the trial's final data for progression-free survival for a protocol unspecified interim time-point, while overall survival is still being monitored. 364 patients with histologically proven colorectal cancer and up to four liver metastases were randomly assigned to either six cycles of FOLFOX4 before and six cycles after surgery or to surgery alone (182 in perioperative chemotherapy group vs 182 in surgery group). Patients were centrally randomised by minimisation, adjusting for centre and risk score. The primary objective was to detect a hazard ratio (HR) of 0.71 or less for progression-free survival. Primary analysis was by intention to treat. Analyses were repeated for all eligible (171 vs 171) and resected patients (151 vs 152). This trial is registered with ClinicalTrials.gov, number NCT00006479.
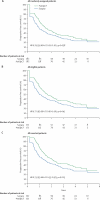
Findings: In the perioperative chemotherapy group, 151 (83%) patients were resected after a median of six (range 1-6) preoperative cycles and 115 (63%) patients received a median six (1-8) postoperative cycles. 152 (84%) patients were resected in the surgery group. The absolute increase in rate of progression-free survival at 3 years was 7.3% (from 28.1% [95.66% CI 21.3-35.5] to 35.4% [28.1-42.7]; HR 0.79 [0.62-1.02]; p=0.058) in randomised patients; 8.1% (from 28.1% [21.2-36.6] to 36.2% [28.7-43.8]; HR 0.77 [0.60-1.00]; p=0.041) in eligible patients; and 9.2% (from 33.2% [25.3-41.2] to 42.4% [34.0-50.5]; HR 0.73 [0.55-0.97]; p=0.025) in patients undergoing resection. 139 patients died (64 in perioperative chemotherapy group vs 75 in surgery group). Reversible postoperative complications occurred more often after chemotherapy than after surgery (40/159 [25%] vs 27/170 [16%]; p=0.04). After surgery we recorded two deaths in the surgery alone group and one in the perioperative chemotherapy group.
Interpretation: Perioperative chemotherapy with FOLFOX4 is compatible with major liver surgery and reduces the risk of events of progression-free survival in eligible and resected patients.
Figures
Comment in
-
Perioperative chemotherapy for resectable hepatic metastases.Lancet. 2008 Mar 22;371(9617):963-5. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60429-8. Lancet. 2008. PMID: 18358910 No abstract available.
-
Surgery vs surgery and chemotherapy for colorectal liver metastases.Lancet. 2008 Jul 19;372(9634):202-3; author report 203. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(08)61063-6. Lancet. 2008. PMID: 18640447 No abstract available.
-
Perioperative or adjuvant therapy for resectable colorectal hepatic metastases.J Clin Oncol. 2008 Oct 20;26(30):4862-3. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.18.5868. Epub 2008 Sep 15. J Clin Oncol. 2008. PMID: 18794535 No abstract available.
References
-
- Nordlinger B, Guiguet M, Vaillant J-C. Surgical resection of colorectal carcinoma metastases to the liver. A prognostic scoring system to improve case selection, based on 1568 patients. Cancer. 1996;77:1254–1262. - PubMed
-
- Giacchetti S, Itzhaki M, Gruia G. Long-term survival of patients with unresectable colorectal cancer liver metastases following infusional chemotherapy with 5-fluorouracil, leucovorin, oxaliplatin and surgery. Ann Oncol. 1999;10:663–669. - PubMed
-
- Andre T, Boni C, Mounedji-Boudiaf L. Oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and leucovorin as adjuvant treatment for colon cancer. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:2343–2351. - PubMed
-
- Lorenz M, Muller HH, Schramm H. Randomized trial of surgery versus surgery followed by adjuvant hepatic arterial infusion with 5-fluorouracil and folinic acid for liver metastases of colorectal cancer. German Cooperative on Liver Metastases (Arbeitsgruppe Lebermetastasen) Ann Surg. 1998;228:756–762. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- 5U10 CA11488-32/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 5U10 CA11488-35/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 5U10-CA11488-28/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 5U10 CA11488-31/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 5U10 CA11488-37/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA011488/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 5U10-CA11488-29/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 5U10 CA11488-34/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 5U10 CA11488-30/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 5U10 CA11488-36/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 5U10 CA11488-33/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

