alpha1-noradrenergic receptor antagonism blocks dependence-induced increases in responding for ethanol
- PMID: 18358987
- PMCID: PMC2587143
- DOI: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2007.12.002
alpha1-noradrenergic receptor antagonism blocks dependence-induced increases in responding for ethanol
Abstract
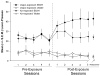
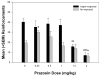
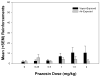
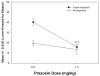
The purpose of this study was to test the hypothesis that blockade of alpha1-adrenergic receptors may suppress the excessive ethanol consumption associated with acute withdrawal in ethanol-dependent rats. Following the acquisition and stabilization of operant ethanol self-administration in male Wistar rats, dependence was induced in half the animals by subjecting them to a 4-week intermittent vapor exposure period in which animals were exposed to ethanol vapor for 14h/day. Subsequent to dependence induction, the effect of alpha1-noradrenergic receptor antagonist prazosin (0.0, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 1.5, and 2.0mg/kg IP) was tested on operant responding for ethanol in vapor-exposed and control rats during acute withdrawal. In ethanol-dependent animals, prazosin significantly suppressed responding at the 1.5 and 2.0mg/kg doses, whereas only the 2.0mg/kg dose was effective in nondependent animals, identifying an increase in the sensitivity to prazosin in dependent animals. Conversely, at the lowest dose tested (0.25mg/kg), prazosin increased responding in nondependent animals, which is consistent with the effect of anxiolytics on ethanol self-administration in nondependent animals. None of the doses tested reliably affected concurrent water self-administration. These results suggest the involvement of the noradrenergic system in the excessive alcohol drinking seen during acute withdrawal in ethanol-dependent rats.
Figures
References
-
- Amit Z, Brown ZW, Levitan DE, Ogren SO. Noradrenergic mediation of the positive reinforcing properties of ethanol: I. Suppression of ethanol consumption in laboratory rats following dopamine-beta-hydroxylase inhibition. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1977;230:65–75. - PubMed
-
- Anderson WW, Thompson T. Ethanol self-administration in water satiated rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1974;2:447–454. - PubMed
-
- Aston-Jones G, Delfs JM, Druhan J, Zhu Y. The bed nucleus of the stria terminalis. A target site for noradrenergic actions in opiate withdrawal. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1999;877:486–498. - PubMed
-
- Aston-Jones G, Harris GC. Brain substrates for increased drug seeking during protracted withdrawal. Neuropharmacology. 2004;47(Suppl 1):167–179. - PubMed
-
- Bozarth MA. Evidence for the rewarding effects of ethanol using the conditioned place preference method. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1990;35:485–487. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

