Nephrolithiasis after bariatric surgery for obesity
- PMID: 18359397
- PMCID: PMC2831413
- DOI: 10.1016/j.semnephrol.2008.01.009
Nephrolithiasis after bariatric surgery for obesity
Abstract
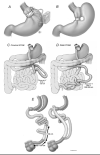
Surgical intervention has become an accepted therapeutic alternative for the patient with medically complicated obesity. Multiple investigators have reported significant and sustained weight loss after bariatric surgery that is associated with improvement of many weight-related medical comorbidities, and statistically significant decreased overall mortality for surgically treated as compared with medically treated subjects. Although the Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) is considered an acceptably safe treatment, an increasing number of patients are being recognized with nephrolithiasis after this, the most common bariatric surgery currently performed. The main risk factor appears to be hyperoxaluria, although low urine volume and citrate concentrations may contribute. The incidence of these urinary risk factors among the total post-RYGB population is unknown, but may be more than previously suspected based on small pilot studies. The etiology of the hyperoxaluria is unknown, but may be related to subtle and seemingly subclinical fat malabsorption. Clearly, further study is needed, especially to define better treatment options than the standard advice for a low-fat, low-oxalate diet, and use of calcium as an oxalate binder.
Figures

References
-
- Demaria EJ, Jamal MK. Surgical options for obesity. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2005;34:127–142. - PubMed
-
- Sarr MG, Felty CL, Hilmer DM, Urban DL, O'Connor G, Hall BA, Rooke TW, Jensen MD. Technical and practical considerations involved in operations on patients weighing more than 270 kg. Arch Surg. 1995;130:102–105. - PubMed
-
- Lopez-Jimenez F, Bhatia S, Collazo-Clavell ML, Sarr MG, Somers VK. Safety and efficacy of bariatric surgery in patients with coronary artery disease. Mayo Clin Proc. 2005;80:1157–1162. - PubMed
-
- Kim TH, Daud A, Ude AO, DiGiorgi M, Olivero-Rivera L, Schrope B, Davis D, Inabnet WB, Bessler M. Early U.S. outcomes of laparoscopic gastric bypass versus laparoscopic adjustable silicone gastric banding for morbid obesity. Surg Endosc. 2006;20:202–209. - PubMed
-
- Mehrotra C, Serdula M, Naimi TS, Khan LK, Miller J, Dietz W. Population-based study of trends, costs, and complications of weight loss surgeries from 1990 to 2002. Obes Res. 2005;13:2029–2034. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

