Therapy of autoimmune bullous diseases
- PMID: 18360613
- PMCID: PMC1936286
- DOI: 10.2147/tcrm.2007.3.1.29
Therapy of autoimmune bullous diseases
Abstract
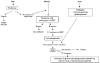
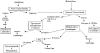
Autoimmune bullous diseases result from an immune response to molecular components of the desmosome or basement membrane. Bullous diseases are associated with a high degree of morbidity and occasional mortality. Therapy of bullous diseases consists of suppressing the immune system, controlling inflammation and improving healing of erosions. The therapeutic agents used in the treatment of bullous diseases may be associated with high morbidity and occasional mortality. Successful treatment requires understanding of the pathophysiology of the disease process and the pharmacology of the drugs being used.
Figures
References
-
- Ahmed AR. Intravenous immunoglobulin therapy in the treatment of patients with pemphigus vulgaris unresponsive to conventional treatment. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001;45:679–90. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed AR, Colon JE. Comparison between intravenous immunoglobulin and conventional immunosuppressive therapy regimens in patients with severe oral pemphigoid. Arch Dermatol. 2001;137:1181–9. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed AR, Moy R. Azathioprine. Int J Dermatol. 1981;20:461–9. - PubMed
-
- Alijotas J, Pedragosa R, Bosch J, et al. Prolonged remission after cyclosporine therapy in pemphigus vulgaris: Report of two young siblings. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1990;23:701–3. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources