Multivariate model of refractive shift in Descemet-stripping automated endothelial keratoplasty
- PMID: 18361978
- PMCID: PMC2796246
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcrs.2007.11.045
Multivariate model of refractive shift in Descemet-stripping automated endothelial keratoplasty
Abstract
Purpose: To relate in situ graft shape in Descemet-stripping automated endothelial keratoplasty (DSAEK) to surgically induced refractive error.
Setting: Academic eye institute.
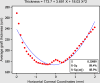
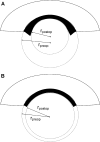
Methods: High frequency arc-scanning ultrasound was performed in 7 patients enrolled in a prospective study of microkeratome-assisted endothelial keratoplasty approved by the Investigative Review Board. A region of interest spanning the horizontal meridian was defined for analysis of epithelial, host, graft, and total corneal thicknesses. Graft thickness profiles were fit by quadratic polynomials where the 2nd-order coefficients represent the posterior corneal curvature contributed by the graft. The curvature coefficient and central graft thickness were analyzed as predictors of induced refractive error.
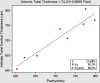
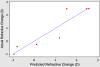
Results: At final follow-up (mean 5.9 months +/- 3.2 [SD]), 3 patients had a hyperopic shift (+2.50 diopters [D] each), 3 had insignificant (< 0.50 D) refractive shifts, and 1 had a myopic shift. In the group with hyperopic shift, a negative lens effect was predicted by positive curvature coefficients, representing grafts that were thinner centrally than peripherally (mean +22.72 microm/mm(2); range +4.95 to +45.17 microm/mm(2)). In the group with minimal refractive shift, coefficients were less positive (mean +7.28 microm/mm(2); range +2.01 to +13.82 microm/mm(2)). The patient with a myopic shift (-1.00 D) had the only negative curvature coefficient (-0.64 microm/mm(2)). In a 2-predictor model of refractive shift, central graft thickness and the curvature coefficient together accounted for 86% of the variance in the refractive response to DSAEK (P = .025).
Conclusion: Nonuniform thickness profiles and variable central graft thicknesses both contribute to refractive shift after DSAEK.
Conflict of interest statement
No author has a financial or proprietary interest in any material or method mentioned.
Figures


References
-
- Gorovoy MS. Descemet-stripping automated endothelial keratoplasty. Cornea. 2006;25:886–889. - PubMed
-
- Price FW, Jr, Price MO. Descemet's stripping with endothelial keratoplasty in 50 eyes: a refractive neutral corneal transplant. J Refract Surg. 2005;21:339–345. - PubMed
-
- Price FW, Jr, Price MO. Descemet's stripping with endothelial keratoplasty in 200 eyes; early challenges and techniques to enhance donor adherence. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2006;32:411–418. - PubMed
-
- Koenig SB, Covert DJ, Dupps WJ, Jr, Meisler DM. Visual acuity, refractive error, and endothelial cell density six months after Descemet stripping and automated endothelial keratoplasty (DSAEK) Cornea. 2007;26:670–674. - PubMed
-
- Covert DJ, Koenig SB. New triple procedure: Descemet's stripping and automated endothelial keratoplasty combined with phacoemulsification and intraocular lens implantation. Ophthalmology. 2007;114:1272–1277. - PubMed

