A composite role of vitronectin and urokinase in the modulation of cell morphology upon expression of the urokinase receptor
- PMID: 18362146
- PMCID: PMC3258879
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.C700214200
A composite role of vitronectin and urokinase in the modulation of cell morphology upon expression of the urokinase receptor
Abstract
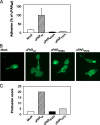
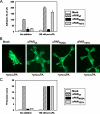
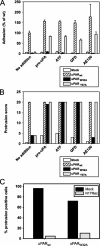
The urokinase receptor, urokinase receptor (uPAR), is a glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored membrane protein engaged in pericellular proteolysis and cellular adhesion, migration, and modulation of cell morphology. A direct matrix adhesion is mediated through the binding of uPAR to vitronectin, and this event is followed by downstream effects including changes in the cytoskeletal organization. However, it remains unclear whether the adhesion through uPAR-vitronectin is the only event capable of initiating these morphological rearrangements or whether lateral interactions between uPAR and integrins can induce the same response. In this report, we show that both of these triggering mechanisms can be operative and that uPAR-dependent modulation of cell morphology can indeed occur independently of a direct vitronectin binding. Expression of wild-type uPAR on HEK293 cells led to pronounced vitronectin adhesion and cytoskeletal rearrangements, whereas a mutant uPAR, uPAR(W32A) with defective vitronectin binding, failed to induce both phenomena. However, upon saturation of uPAR(W32A) with the protease ligand, pro-uPA, or its receptor-binding domain, the ability to induce cytoskeletal rearrangements was restored, although this did not rescue the uPAR-vitronectin binding and adhesion capability. On the other hand, using other uPAR variants, we could show that uPAR-vitronectin adhesion is indeed capable and sufficient to induce the same morphological rearrangements. This was shown with cells expressing a different single-site mutant, uPAR(Y57A), in the presence of a synthetic uPAR-binding peptide, as well as with wild-type uPAR, which underwent cytoskeletal rearrangements even when cultivated in uPA-deficient serum. Blocking of integrins with an Arg-Gly-Asp-containing peptide counteracted the matrix contacts necessary to initiate the uPAR-dependent cytoskeletal rearrangements, whereas inactivation of the Rac signaling pathway in all cases suppressed the occurrence of the same events.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A new class of orthosteric uPAR·uPA small-molecule antagonists are allosteric inhibitors of the uPAR·vitronectin interaction.ACS Chem Biol. 2015 Jun 19;10(6):1521-34. doi: 10.1021/cb500832q. Epub 2015 Mar 31. ACS Chem Biol. 2015. PMID: 25671694 Free PMC article.
-
Requirement of receptor-bound urokinase-type plasminogen activator for integrin alphavbeta5-directed cell migration.J Biol Chem. 1996 Nov 15;271(46):29393-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.46.29393. J Biol Chem. 1996. PMID: 8910604
-
The uPA receptor and the somatomedin B region of vitronectin direct the localization of uPA to focal adhesions in microvessel endothelial cells.Matrix Biol. 2007 Jun;26(5):359-70. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2007.01.009. Epub 2007 Feb 6. Matrix Biol. 2007. PMID: 17344041
-
Structure, function and expression on blood and bone marrow cells of the urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor, uPAR.Stem Cells. 1997;15(6):398-408. doi: 10.1002/stem.150398. Stem Cells. 1997. PMID: 9402652 Review.
-
Biological significance of the expression of urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptors (uPARs) in brain tumors.Front Biosci. 1999 Feb 15;4:D178-87. doi: 10.2741/mohanam. Front Biosci. 1999. PMID: 9989951 Review.
Cited by
-
Human antibody VH domains targeting uPAR as candidate therapeutics for cancers.Front Oncol. 2023 Oct 9;13:1194972. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1194972. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37876962 Free PMC article.
-
Vitronectin and Urokinase-Type Plasminogen Activator Gene Expression Levels Are Increased in Patients with Coronary Artery In-Stent Restenosis.Int J Angiol. 2017 Dec;26(4):218-222. doi: 10.1055/s-0037-1601871. Epub 2017 Apr 16. Int J Angiol. 2017. PMID: 29142486 Free PMC article.
-
Urokinase-type plasminogen activator inhibits efferocytosis of neutrophils.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2010 Dec 15;182(12):1516-23. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201003-0452OC. Epub 2010 Jul 23. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2010. PMID: 20656938 Free PMC article.
-
Serum-stable RNA aptamers to urokinase-type plasminogen activator blocking receptor binding.RNA. 2010 Dec;16(12):2360-9. doi: 10.1261/rna.2338210. Epub 2010 Oct 20. RNA. 2010. PMID: 20962041 Free PMC article.
-
A new class of orthosteric uPAR·uPA small-molecule antagonists are allosteric inhibitors of the uPAR·vitronectin interaction.ACS Chem Biol. 2015 Jun 19;10(6):1521-34. doi: 10.1021/cb500832q. Epub 2015 Mar 31. ACS Chem Biol. 2015. PMID: 25671694 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

