The silent information regulator 3 protein, SIR3p, binds to chromatin fibers and assembles a hypercondensed chromatin architecture in the presence of salt
- PMID: 18362167
- PMCID: PMC2423291
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01389-07
The silent information regulator 3 protein, SIR3p, binds to chromatin fibers and assembles a hypercondensed chromatin architecture in the presence of salt
Abstract
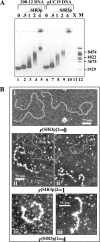
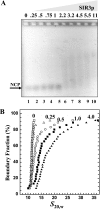
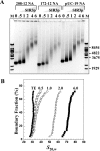
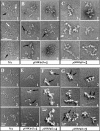
The telomeres and mating-type loci of budding yeast adopt a condensed, heterochromatin-like state through recruitment of the silent information regulator (SIR) proteins SIR2p, SIR3p, and SIR4p. In this study we characterize the chromatin binding determinants of recombinant SIR3p and identify how SIR3p mediates chromatin fiber condensation in vitro. Purified full-length SIR3p was incubated with naked DNA, nucleosome core particles, or defined nucleosomal arrays, and the resulting complexes were analyzed by electrophoretic shift assays, sedimentation velocity, and electron microscopy. SIR3p bound avidly to all three types of templates. SIR3p loading onto its nucleosomal sites in chromatin produced thickened condensed fibers that retained a beaded morphology. At higher SIR3p concentrations, individual nucleosomal arrays formed oligomeric suprastructures bridged by SIR3p oligomers. When condensed SIR3p-bound chromatin fibers were incubated in Mg(2+), they folded and oligomerized even further to produce hypercondensed higher-order chromatin structures. Collectively, these results define how SIR3p may function as a chromatin architectural protein and provide new insight into the interplay between endogenous and protein-mediated chromatin fiber condensation pathways.
Figures
References
-
- Adams, V. H., S. J. McBryant, P. H. Wade, C. Woodcock, and J. C. Hansen. 2007. Intrinsic disorder and autonomous domain function in the multifunctional nuclear protein, MeCP2. J. Biol. Chem. 28215057-15064. - PubMed
-
- Adkins, N. L., M. Watts, and P. T. Georgel. 2004. To the 30-nm chromatin fiber and beyond. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 167712-23. - PubMed
-
- Ausio, J., D. Seger, and H. Eisenberg. 1984. Nucleosome core particle stability and conformational change: effect of temperature, particle and NaCl concentrations, and cross-linking of histone H3 sulfhydryl groups. J. Mol. Biol. 17677-104. - PubMed
-
- Barbera, A. J., J. V. Chodaparambil, B. Kelley-Clarke, V. Joukov, J. C. Walter, K. Luger, and K. M. Kaye. 2006. The nucleosomal surface as a docking station for Kaposi's sarcoma herpesvirus LANA. Science 311856-861. - PubMed
-
- Bednar, J., R. A. Horowitz, S. A. Grigoryev, L. M. Carruthers, J. C. Hansen, A. J. Koster, and C. L. Woodcock. 1998. Nucleosomes, linker DNA, and linker histone form a unique structural motif that directs the higher-order folding and compaction of chromatin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 9514173-14178. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
