Arginine regulation by myeloid derived suppressor cells and tolerance in cancer: mechanisms and therapeutic perspectives
- PMID: 18364002
- PMCID: PMC3546504
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2008.00608.x
Arginine regulation by myeloid derived suppressor cells and tolerance in cancer: mechanisms and therapeutic perspectives
Abstract
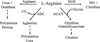
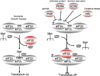
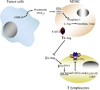
Patients with cancer have an impaired T-cell response that can decrease the potential therapeutic benefit of cancer vaccines and other forms of immunotherapy. L-arginine (L-Arg) is a conditionally essential amino acid that is fundamental for the function of T lymphocytes. Recent findings in tumor-bearing mice and cancer patients indicate that increased metabolism of L-Arg by myeloid derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) producing arginase I inhibits T-lymphocyte responses. Here we discuss some of the most recent concepts how MDSC expressing arginase I may regulate T-cell function in cancer and other chronic inflammatory diseases and suggest possible therapeutic interventions to overcome this inhibitory effect.
Figures
References
-
- Miescher S, Whiteside TL, Carrel S, von FV. Functional properties of tumor-infiltrating and blood lymphocytes in patients with solid tumors: effects of tumor cells and their supernatants on proliferative responses of lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1986;136:1899–1907. - PubMed
-
- Miescher S, Stoeck M, Qiao L, Barras C, Barrelet L, von Fliedner V. Preferential clonogenic deficit of CD8-positive T-lymphocytes infiltrating human solid tumors. Cancer Res. 1988;48:6992–6998. - PubMed
-
- Whiteside TL, Miescher S, Moretta L, von Fliedner V. Cloning and proliferating precursor frequencies of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes from human solid tumors. Transplant Proc. 1988;20:342–343. - PubMed
-
- Hellstrom I, Sjogren HO, Warner G, Hellstrom KE. Blocking of cell-mediated tumor immunity by sera from patients with growing neoplasms. Int J Cancer. 1971;7:226–237. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

