Characterization of VAR2CSA-deficient Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes selected for adhesion to the BeWo placental cell line
- PMID: 18364051
- PMCID: PMC2329659
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2875-7-51
Characterization of VAR2CSA-deficient Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes selected for adhesion to the BeWo placental cell line
Abstract
Background: Malaria in pregnancy is characterized by accumulation of infected erythrocytes (IE) in the placenta. The key ligand identified as mediating this process is a Plasmodium falciparum erythrocyte membrane protein 1 family member, termed VAR2CSA. VAR2CSA appears to be the main ligand responsible for adhesion to chondroitin sulphate A (CSA). Whether other PfEMP1 molecules can also mediate placental adhesion, independent of CSA binding, is unclear.
Methods: The parasite line CS2 carrying a disrupted var2csa gene (CS2KO) was selected for adhesion to the BeWo choriocarcinoma cell line, which has been proposed as a model for placental malaria. The selected and control IE were tested for adhesion to placental sections and flow cytometry was used to measure recognition of IE by three serum sets from malaria-exposed men and women.
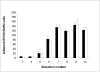
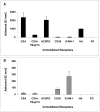
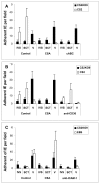
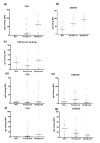
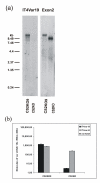
Results: Wild-type CS2 adhere to BeWo and placental tissue via CSA. CS2KO IE were successfully selected for adhesion to BeWo, and adhered by a CSA-independent mechanism. They bound to immobilized ICAM-1 and CD36. BeWo-selected CS2KO bound at moderate levels to placental sections, but most binding was to placental villi rather than to the syncytiotrophoblast to which IE adherence occurs in vivo. This binding was inhibited by a blocking antibody to CD36 but not to ICAM-1. As expected, sera from malaria-exposed adults recognized CS2 IE in a gender and parity dependent manner. In one serum set, there was a similar but less pronounced pattern of antibody binding to selected CS2KO IE, but this was not seen in two others. One var gene, It4var19, was particularly abundant in the selected line and was detected as full length transcripts in BeWo-selected IE, but not unselected CS2KO.
Conclusion: This study suggests that IE with characteristics similar to the CS2KO have a limited role in the pathogenesis of placental malaria. VAR2CSA appear to be the major ligand for placental adhesion, and could be the basis for a vaccine against pregnancy malaria.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Disruption of var2csa gene impairs placental malaria associated adhesion phenotype.PLoS One. 2007 Sep 19;2(9):e910. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0000910. PLoS One. 2007. PMID: 17878945 Free PMC article.
-
Antibodies from malaria-exposed pregnant women recognize trypsin resistant epitopes on the surface of Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes selected for adhesion to chondroitin sulphate A.Malar J. 2004 Sep 6;3:31. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-3-31. Malar J. 2004. PMID: 15350207 Free PMC article.
-
Chondroitin sulphate A (CSA)-binding of single recombinant Duffy-binding-like domains is not restricted to Plasmodium falciparum Erythrocyte Membrane Protein 1 expressed by CSA-binding parasites.Int J Parasitol. 2009 Sep;39(11):1195-204. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2009.02.022. Epub 2009 Mar 24. Int J Parasitol. 2009. PMID: 19324047
-
Cytoadhesion of Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes and the infected placenta: a two-way pathway.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2006 Dec;39(12):1525-36. doi: 10.1590/s0100-879x2006001200003. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2006. PMID: 17160261 Review.
-
Designing a VAR2CSA-based vaccine to prevent placental malaria.Vaccine. 2015 Dec 22;33(52):7483-8. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2015.10.011. Epub 2015 Nov 26. Vaccine. 2015. PMID: 26469717 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The role of platelets in the pathogenesis of cerebral malaria.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2010 Feb;67(4):557-68. doi: 10.1007/s00018-009-0211-3. Epub 2009 Nov 29. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2010. PMID: 20091081 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prospects and Pitfalls of Pregnancy-Associated Malaria Vaccination Based on the Natural Immune Response to Plasmodium falciparum VAR2CSA-Expressing Parasites.Malar Res Treat. 2011;2011:764845. doi: 10.4061/2011/764845. Epub 2012 Jan 18. Malar Res Treat. 2011. PMID: 22363896 Free PMC article.
-
An image-based drug susceptibility assay targeting the placental sequestration of Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes.PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e41765. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0041765. Epub 2012 Aug 29. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22952585 Free PMC article.
-
Placental Sequestration of Plasmodium falciparum Malaria Parasites Is Mediated by the Interaction Between VAR2CSA and Chondroitin Sulfate A on Syndecan-1.PLoS Pathog. 2016 Aug 24;12(8):e1005831. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005831. eCollection 2016 Aug. PLoS Pathog. 2016. PMID: 27556547 Free PMC article.
-
Poor Birth Outcomes in Malaria in Pregnancy: Recent Insights Into Mechanisms and Prevention Approaches.Front Immunol. 2021 Mar 15;12:621382. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.621382. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33790894 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Steketee RW, Nahlen BL, Parise ME, Menendez C. The burden of malaria in pregnancy in malaria-endemic areas. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2001;64:28–35. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

