The vitamin D receptor is required for iNKT cell development
- PMID: 18364394
- PMCID: PMC2278204
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0711558105
The vitamin D receptor is required for iNKT cell development
Abstract
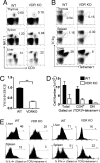
CD1d-reactive natural killer T (NKT) cells with an invariant T cell receptor Valpha14 rearrangement are a unique subset of lymphocytes, which play important roles in immune regulation, tumor surveillance, and host defense against pathogens. Vitamin D is a nutrient/hormone that has been shown to regulate conventional T cell responses but not T cell development. The data show that expression of the vitamin D receptor (VDR) is required for normal development and function of iNKT cells. The iNKT cells from VDR KO mice are intrinsically defective and lack T-bet expression. VDR KO iNKT cells fail to express NK1.1, although they express normal levels of CD122. Extrinsic factors that impact iNKT cell development and function in VDR KO mice include a failure of the liver to support homeostatic proliferation and reduced thymic expression of CD1d and other factors important for optimal antigen presentation in the thymus. In addition, VDR KO iNKT cells were intrinsically defective even when WT antigen-presenting cells were used to stimulate them.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
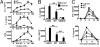



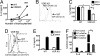
References
-
- Godfrey DI, Hammond KJ, Poulton LD, Smyth MJ, Baxter AG. NKT cells: Facts, functions and fallacies. Immunol Today. 2000;21:573–583. - PubMed
-
- Bendelac A, Bonneville M, Kearney JF. Autoreactivity by design: Innate B and T lymphocytes. Nat Rev Immunol. 2001;1:177–186. - PubMed
-
- Taniguchi M, Harada M, Kojo S, Nakayama T, Wakao H. The regulatory role of Valpha14 NKT cells in innate and acquired immune response. Annu Rev Immunol. 2003;21:483–513. - PubMed
-
- Bendelac A, Rivera MN, Park SH, Roark JH. Mouse CD1-specific NK1 T cells: Development, specificity, and function. Annu Rev Immunol. 1997;15:535–562. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

