Organization of multiprotein complexes at cell-cell junctions
- PMID: 18365233
- PMCID: PMC2413109
- DOI: 10.1007/s00418-008-0418-7
Organization of multiprotein complexes at cell-cell junctions
Abstract
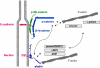
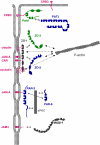
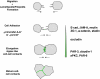
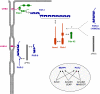
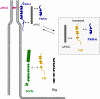
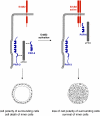
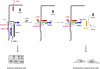
The formation of stable cell-cell contacts is required for the generation of barrier-forming sheets of epithelial and endothelial cells. During various physiological processes like tissue development, wound healing or tumorigenesis, cellular junctions are reorganized to allow the release or the incorporation of individual cells. Cell-cell contact formation is regulated by multiprotein complexes which are localized at specific structures along the lateral cell junctions like the tight junctions and adherens junctions and which are targeted to these site through their association with cell adhesion molecules. Recent evidence indicates that several major protein complexes exist which have distinct functions during junction formation. However, this evidence also indicates that their composition is dynamic and subject to changes depending on the state of junction maturation. Thus, cell-cell contact formation and integrity is regulated by a complex network of protein complexes. Imbalancing this network by oncogenic proteins or pathogens results in barrier breakdown and eventually in cancer. Here, I will review the molecular organization of the major multiprotein complexes at junctions of epithelial cells and discuss their function in cell-cell contact formation and maintenance.
Figures
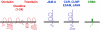


References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PMC', 'value': 'PMC2133977', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2133977/'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '8991100', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8991100/'}]}
- Adams CL, Nelson WJ, Smith SJ (1996) Quantitative analysis of cadherin-catenin-actin reorganization during development of cell–cell adhesion. J Cell Biol 135:1899–1911 - PMC - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PMC', 'value': 'PMC3369828', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3369828/'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '12775840', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12775840/'}]}
- Amieva MR, Vogelmann R, Covacci A, Tompkins LS, Nelson WJ, Falkow S (2003) Disruption of the epithelial apical-junctional complex by Helicobacter pylori CagA. Science 300:1430–1434 - PMC - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '9299162', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9299162/'}]}
- Aoki J, Koike S, Asou H, Ise I, Suwa H, Tanaka T, Miyasaka M, Nomoto A (1997) Mouse homolog of poliovirus receptor-related gene 2 product, mPRR2, mediates homophilic cell aggregation. Exp Cell Res 235:374–384 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '17060907', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17060907/'}]}
- Aranda V, Haire T, Nolan ME, Calarco JP, Rosenberg AZ, Fawcett JP, Pawson T, Muthuswamy SK (2006) Par6-aPKC uncouples ErbB2 induced disruption of polarized epithelial organization from proliferation control. Nat Cell Biol 8:1235–1245 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '12446711', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12446711/'}]}
- Asada M, Irie K, Morimoto K, Yamada A, Ikeda W, Takeuchi M, Takai Y (2003) ADIP, a novel Afadin- and alpha-actinin-binding protein localized at cell–cell adherens junctions. J Biol Chem 278:4103–4111 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

