Structure and function of mammalian cilia
- PMID: 18365235
- PMCID: PMC2386530
- DOI: 10.1007/s00418-008-0416-9
Structure and function of mammalian cilia
Abstract
In the past half century, beginning with electron microscopic studies of 9 + 2 motile and 9 + 0 primary cilia, novel insights have been obtained regarding the structure and function of mammalian cilia. All cilia can now be viewed as sensory cellular antennae that coordinate a large number of cellular signaling pathways, sometimes coupling the signaling to ciliary motility or alternatively to cell division and differentiation. This view has had unanticipated consequences for our understanding of developmental processes and human disease.
Figures
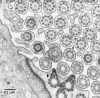
References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1002/path.1652', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1002/path.1652'}, {'type': 'PMC', 'value': 'PMC7167937', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7167937/'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '15495266', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15495266/'}]}
- Afzelius BA (2004) Cilia-related diseases. J Pathol 204:470–477 - PMC - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PMC', 'value': 'PMC1271007', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC1271007/'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '5105129', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/5105129/'}]}
- Archer FL, Wheatley DN (1971) Cilia in cell-cultured fibroblasts. II. Incidence in mitotic and post-mitotic BHK 21-C13 fibroblasts. J Anat 109:277–292 - PMC - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1016/S0092-8674(04)00412-X', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(04)00412-x'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '15137945', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15137945/'}]}
- Avidor-Reiss T, Maer AM, Koundakjian E, Polyanovsky A, Keil T, Subramaniam S, Zuker CS (2004) Decoding cilia function: defining specialized genes required for compartmentalized cilia biogenesis. Cell 117:527–539 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1146/annurev.genom.7.080505.115610', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.genom.7.080505.115610'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '16722803', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16722803/'}]}
- Badano JL, Mitsuma N, Beales PL, Katsanis N (2006) The ciliopathies: an emerging class of human genetic disorders. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet 7:125–148 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1074/jbc.M300156200', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.m300156200'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '12821668', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12821668/'}]}
- Baker SA, Freeman K, Luby-Phelps K, Pazour GJ, Besharse JC (2003) IFT20 links kinesin II with a mammalian intraflagellar transport complex that is conserved in motile flagella and sensory cilia. J Biol Chem 278:34211–34218 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

