E2f6 and Bmi1 cooperate in axial skeletal development
- PMID: 18366140
- PMCID: PMC2697036
- DOI: 10.1002/dvdy.21516
E2f6 and Bmi1 cooperate in axial skeletal development
Abstract
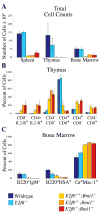
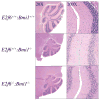
Bmi1 is a Polycomb Group protein that functions as a component of Polycomb Repressive Complex 1 (PRC1) to control axial skeleton development through Hox gene repression. Bmi1 also represses transcription of the Ink4a-Arf locus and is consequently required to maintain the proliferative and self-renewal properties of hematopoietic and neural stem cells. Previously, one E2F family member, E2F6, has been shown to interact with Bmi1 and other known PRC1 components. However, the biological relevance of this interaction is unknown. In this study, we use mouse models to investigate the interplay between E2F6 and Bmi1. This analysis shows that E2f6 and Bmi1 cooperate in the regulation of Hox genes, and consequently axial skeleton development, but not in the repression of the Ink4a-Arf locus. These findings underscore the significance of the E2F6-Bmi1 interaction in vivo and suggest that the Hox and Ink4a-Arf loci are regulated by somewhat different mechanisms.
Figures




References
-
- Adler PN, Martin EC, Charlton J, Jones K. Phenotypic consequences and genetic interactions of a null mutation in the Drosophila Posterior Sex Combs gene. Dev Genet. 1991;12:349–361. - PubMed
-
- Akasaka T, Kanno M, Balling R, Mieza MA, Taniguchi M, Koseki H. A role for mel-18, a Polycomb group-related vertebrate gene, during theanteroposterior specification of the axial skeleton. Development. 1996;122:1513–1522. - PubMed
-
- Akasaka T, Tsuji K, Kawahira H, Kanno M, Harigaya K, Hu L, Ebihara Y, Nakahata T, Tetsu O, Taniguchi M, Koseki H. The role of mel-18, a mammalian Polycomb group gene, during IL-7-dependent proliferation of lymphocyte precursors. Immunity. 1997;7:135–146. - PubMed
-
- Akasaka T, van Lohuizen M, van der Lugt N, Mizutani-Koseki Y, Kanno M, Taniguchi M, Vidal M, Alkema M, Berns A, Koseki H. Mice doubly deficient for the Polycomb Group genes Mel18 and Bmi1 reveal synergy and requirement for maintenance but not initiation of Hox gene expression. Development. 2001;128:1587–1597. - PubMed
-
- Alkema MJ, Bronk M, Verhoeven E, Otte A, van ’t Veer LJ, Berns A, van Lohuizen M. Identification of Bmi1-interacting proteins as constituents of a multimeric mammalian polycomb complex. Genes Dev. 1997;11:226–240. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

