Analysis of the cryptophycin P450 epoxidase reveals substrate tolerance and cooperativity
- PMID: 18366166
- PMCID: PMC2697446
- DOI: 10.1021/ja710520q
Analysis of the cryptophycin P450 epoxidase reveals substrate tolerance and cooperativity
Abstract
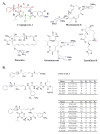
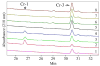
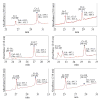
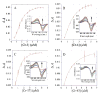
Cryptophycins are potent anticancer agents isolated from Nostoc sp. ATCC 53789 and Nostoc sp. GSV 224. The most potent natural cryptophycin analogues retain a beta-epoxide at the C2'-C3' position of the molecule. A P450 epoxidase encoded by c rpE recently identified from the cryptophycin gene cluster was shown to install this key functional group into cryptophycin-4 (Cr-4) to produce cryptophycin-2 (Cr-2) in a regio- and stereospecific manner. Here we report a detailed characterization of the CrpE epoxidase using an engineered maltose binding protein (MBP)-CrpE fusion. The substrate tolerance of the CrpE polypeptide was investigated with a series of structurally related cryptophycin analogues generated by chemoenzymatic synthesis. The enzyme specifically installed a beta-epoxide between C2' and C3' of cyclic cryptophycin analogues. The kcat/Km values of the enzyme were determined to provide further insights into the P450 epoxidase catalytic efficiency affected by substrate structural variation. Finally, binding analysis revealed cooperativity of MBP-CrpE toward natural and unnatural desepoxy cryptophycin substrates.
Figures

References
-
- Welker M, von Dohren H. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2006;30:530–563. - PubMed
-
- Clardy J, Fischbach MA, Walsh CT. Nat Biotechnol. 2006;24:1541–1550. - PubMed
-
- Golakoti T, Yoshida WY, Chaganty S, Moore RE. J Nat Prod. 2001;64:54–59. - PubMed
-
- Schwartz RE, Hirsch CF, Sesin DF, Flor JE, Chartrain M, Fromtling RE, Harris GH, Salvatore MJ, Liesch JM, Yudin K. J Indust Microbiol. 1990;5:113–123.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

