Differences in the selection response of serially repeated color pattern characters: standing variation, development, and evolution
- PMID: 18366752
- PMCID: PMC2322975
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2148-8-94
Differences in the selection response of serially repeated color pattern characters: standing variation, development, and evolution
Abstract
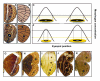
Background: There is spectacular morphological diversity in nature but lineages typically display a limited range of phenotypes. Because developmental processes generate the phenotypic variation that fuels natural selection, they are a likely source of evolutionary biases, facilitating some changes and limiting others. Although shifts in developmental regulation are associated with morphological differences between taxa, it is unclear how underlying mechanisms affect the rate and direction of evolutionary change within populations under selection. Here we focus on two ecologically relevant features of butterfly wing color patterns, eyespot size and color composition, which are similarly and strongly correlated across the serially repeated eyespots. Though these two characters show similar patterns of standing variation and covariation within a population, they differ in key features of their underlying development. We targeted pairs of eyespots with artificial selection for coordinated (concerted selection) versus independent (antagonistic selection) change in their color composition and size and compared evolutionary responses of the two color pattern characters.
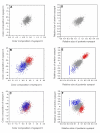
Results: The two characters respond to selection in strikingly different ways despite initially similar patterns of variation in all directions present in the starting population. Size (determined by local properties of a diffusing inductive signal) evolves flexibly in all selected directions. However, color composition (determined by a tissue-level response to the signal concentration gradient) evolves only in the direction of coordinated change. There was no independent evolutionary change in the color composition of two eyespots in response to antagonistic selection. Moreover, these differences in the directions of short-term evolutionary change in eyespot size and color composition within a single species are consistent with the observed wing pattern diversity in the genus.
Conclusion: Both characters respond rapidly to selection for coordinated change, but there are striking differences in their response to selection for antagonistic, independent change across eyespots. While many additional factors may contribute to both short- and long-term evolutionary response, we argue that the compartmentalization of developmental processes can influence the diversification of serial repeats such as butterfly eyespots, even under strong selection.
Figures


References
-
- Muller GB, Wagner GP. Novelty in Evolution - Restructuring the Concept. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics. 1991;22:229–256. doi: 10.1146/annurev.es.22.110191.001305. - DOI
-
- Alberch P. Ontogenesis and morphological diversification. American Zoologist. 1980;20(4):653–667.
-
- McGhee GR. The Geometry of Evolution: Adaptive Landscapes and Theoretical Morphospaces. Cambridge , Cambridge University Press; 2007.
-
- Alberch P. Developmental constraints: why St. Bernards often have an extra digit and poodles never do. American Naturalist. 1985;126(3):430–433. doi: 10.1086/284428. - DOI
-
- Blows MW, Hoffmann AA. A reassessment of genetic limits to evolutionary change. Ecology. 2005;86(6):1371–1384. doi: 10.1890/04-1209. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

