PSAT: a web tool to compare genomic neighborhoods of multiple prokaryotic genomes
- PMID: 18366802
- PMCID: PMC2358893
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-9-170
PSAT: a web tool to compare genomic neighborhoods of multiple prokaryotic genomes
Abstract
Background: The conservation of gene order among prokaryotic genomes can provide valuable insight into gene function, protein interactions, or events by which genomes have evolved. Although some tools are available for visualizing and comparing the order of genes between genomes of study, few support an efficient and organized analysis between large numbers of genomes. The Prokaryotic Sequence homology Analysis Tool (PSAT) is a web tool for comparing gene neighborhoods among multiple prokaryotic genomes.
Results: PSAT utilizes a database that is preloaded with gene annotation, BLAST hit results, and gene-clustering scores designed to help identify regions of conserved gene order. Researchers use the PSAT web interface to find a gene of interest in a reference genome and efficiently retrieve the sequence homologs found in other bacterial genomes. The tool generates a graphic of the genomic neighborhood surrounding the selected gene and the corresponding regions for its homologs in each comparison genome. Homologs in each region are color coded to assist users with analyzing gene order among various genomes. In contrast to common comparative analysis methods that filter sequence homolog data based on alignment score cutoffs, PSAT leverages gene context information for homologs, including those with weak alignment scores, enabling a more sensitive analysis. Features for constraining or ordering results are designed to help researchers browse results from large numbers of comparison genomes in an organized manner. PSAT has been demonstrated to be useful for helping to identify gene orthologs and potential functional gene clusters, and detecting genome modifications that may result in loss of function.
Conclusion: PSAT allows researchers to investigate the order of genes within local genomic neighborhoods of multiple genomes. A PSAT web server for public use is available for performing analyses on a growing set of reference genomes through any web browser with no client side software setup or installation required. Source code is freely available to researchers interested in setting up a local version of PSAT for analysis of genomes not available through the public server. Access to the public web server and instructions for obtaining source code can be found at http://www.nwrce.org/psat.
Figures
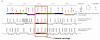
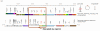

Similar articles
-
A universal operon predictor for prokaryotic genomes.J Bioinform Comput Biol. 2009 Feb;7(1):19-38. doi: 10.1142/s0219720009003984. J Bioinform Comput Biol. 2009. PMID: 19226658
-
Prokaryotic gene prediction using GeneMark and GeneMark.hmm.Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. 2003 May;Chapter 4:Unit4.5. doi: 10.1002/0471250953.bi0405s01. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. 2003. PMID: 18428700
-
GenomeBlast: a web tool for small genome comparison.BMC Bioinformatics. 2006 Dec 12;7 Suppl 4(Suppl 4):S18. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-7-S4-S18. BMC Bioinformatics. 2006. PMID: 17217510 Free PMC article.
-
An overview of the wcd EST clustering tool.Bioinformatics. 2008 Jul 1;24(13):1542-6. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btn203. Epub 2008 May 14. Bioinformatics. 2008. PMID: 18480101 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modern technologies and algorithms for scaffolding assembled genomes.PLoS Comput Biol. 2019 Jun 5;15(6):e1006994. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1006994. eCollection 2019 Jun. PLoS Comput Biol. 2019. PMID: 31166948 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Short and long-term genome stability analysis of prokaryotic genomes.BMC Genomics. 2013 May 8;14:309. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-309. BMC Genomics. 2013. PMID: 23651581 Free PMC article.
-
What Makes a Bacterial Species Pathogenic?:Comparative Genomic Analysis of the Genus Leptospira.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2016 Feb 18;10(2):e0004403. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0004403. eCollection 2016 Feb. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2016. PMID: 26890609 Free PMC article.
-
Detecting sequence homology at the gene cluster level with MultiGeneBlast.Mol Biol Evol. 2013 May;30(5):1218-23. doi: 10.1093/molbev/mst025. Epub 2013 Feb 14. Mol Biol Evol. 2013. PMID: 23412913 Free PMC article.
-
Pan-genome sequence analysis using Panseq: an online tool for the rapid analysis of core and accessory genomic regions.BMC Bioinformatics. 2010 Sep 15;11:461. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-11-461. BMC Bioinformatics. 2010. PMID: 20843356 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Gene Expression Patterns of Yersinia pestis and Yersinia pseudotuberculosis during Infection and Biofilm Formation in the Flea Digestive Tract.mSystems. 2019 Feb 19;4(1):e00217-18. doi: 10.1128/mSystems.00217-18. eCollection 2019 Jan-Feb. mSystems. 2019. PMID: 30801031 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

