State-dependent bidirectional modification of somatic inhibition in neocortical pyramidal cells
- PMID: 18367091
- PMCID: PMC2880402
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2008.01.030
State-dependent bidirectional modification of somatic inhibition in neocortical pyramidal cells
Abstract
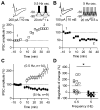
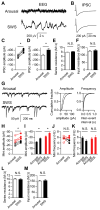
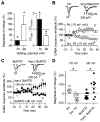
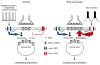
Cortical pyramidal neurons alter their responses to input signals depending on behavioral state. We investigated whether changes in somatic inhibition contribute to these alterations. In layer 5 pyramidal neurons of rat visual cortex, repetitive firing from a depolarized membrane potential, which typically occurs during arousal, produced long-lasting depression of somatic inhibition. In contrast, slow membrane oscillations with firing in the depolarized phase, which typically occurs during slow-wave sleep, produced long-lasting potentiation. The depression is mediated by L-type Ca2+ channels and GABA(A) receptor endocytosis, whereas potentiation is mediated by R-type Ca2+ channels and receptor exocytosis. It is likely that the direction of modification is mainly dependent on the ratio of R- and L-type Ca2+ channel activation. Furthermore, somatic inhibition was stronger in slices prepared from rats during slow-wave sleep than arousal. This bidirectional modification of somatic inhibition may alter pyramidal neuron responsiveness in accordance with behavioral state.
Figures

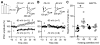
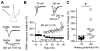
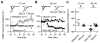
Comment in
-
All asleep-but inhibition is wide awake.Neuron. 2008 Mar 27;57(6):804-6. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2008.03.010. Neuron. 2008. PMID: 18367080
Similar articles
-
GABA actions in hippocampal area CA3 during postnatal development: differential shift from depolarizing to hyperpolarizing in somatic and dendritic compartments.J Neurophysiol. 2008 Mar;99(3):1523-34. doi: 10.1152/jn.01074.2007. Epub 2008 Jan 23. J Neurophysiol. 2008. PMID: 18216229
-
SK channel regulation of dendritic excitability and dendrodendritic inhibition in the olfactory bulb.J Neurophysiol. 2005 Dec;94(6):3743-50. doi: 10.1152/jn.00797.2005. Epub 2005 Aug 17. J Neurophysiol. 2005. PMID: 16107526
-
Dynamic modulation of excitation and inhibition during stimulation at gamma and beta frequencies in the CA1 hippocampal region.J Neurophysiol. 2001 Jun;85(6):2412-22. doi: 10.1152/jn.2001.85.6.2412. J Neurophysiol. 2001. PMID: 11387387
-
Dendritic spikes in apical dendrites of neocortical layer 2/3 pyramidal neurons.J Neurosci. 2007 Aug 22;27(34):8999-9008. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1717-07.2007. J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17715337 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the NMDA component of EPSPs by different components of postsynaptic GABAergic inhibition: computer simulation analysis in piriform cortex.J Neurophysiol. 1997 Nov;78(5):2546-59. doi: 10.1152/jn.1997.78.5.2546. J Neurophysiol. 1997. PMID: 9356404
Cited by
-
Stabilization of GABA(A) receptors at endocytic zones is mediated by an AP2 binding motif within the GABA(A) receptor β3 subunit.J Neurosci. 2012 Feb 15;32(7):2485-98. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1622-11.2011. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22396422 Free PMC article.
-
CA1 pyramidal cell theta-burst firing triggers endocannabinoid-mediated long-term depression at both somatic and dendritic inhibitory synapses.J Neurosci. 2013 Aug 21;33(34):13743-57. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0817-13.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23966696 Free PMC article.
-
Diurnal inhibition of NMDA-EPSCs at rat hippocampal mossy fibre synapses through orexin-2 receptors.J Physiol. 2014 Oct 1;592(19):4277-95. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2014.272757. Epub 2014 Aug 1. J Physiol. 2014. PMID: 25085886 Free PMC article.
-
Biophysical Modeling of Frontocentral ERP Generation Links Circuit-Level Mechanisms of Action-Stopping to a Behavioral Race Model.J Neurosci. 2024 May 15;44(20):e2016232024. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2016-23.2024. J Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38561227 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory Plasticity: From Molecules to Computation and Beyond.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Mar 6;21(5):1805. doi: 10.3390/ijms21051805. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32155701 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abraham WC, Bear MF. Metaplasticity: the plasticity of synaptic plasticity. Trends Neurosci. 1996;19:126–130. - PubMed
-
- Aizenman CD, Manis PB, Linden DJ. Polarity of long-term synaptic gain change is related to postsynaptic spike firing at a cerebellar inhibitory synapse. Neuron. 1998;21:827–835. - PubMed
-
- Artola A, Singer W. Long-term depression of excitatory synaptic transmission and its relationship to long-term potentiation. Trends Neurosci. 1993;16:480–487. - PubMed
-
- Barnes EM. Intracellular trafficking of GABAA receptors. Life Sci. 2000;66:1063–1070. - PubMed
-
- Bear MF, Abraham WC. Long-term depression in hippocampus. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1996;19:437–462. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

