Dysregulation of nociceptin/orphanin FQ activity in the amygdala is linked to excessive alcohol drinking in the rat
- PMID: 18367152
- PMCID: PMC4275225
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2008.02.004
Dysregulation of nociceptin/orphanin FQ activity in the amygdala is linked to excessive alcohol drinking in the rat
Abstract
Background: Alcoholism is a complex behavioral disorder in which interactions between stressful life events and heritable susceptibility factors contribute to the initiation and progression of disease. Neural substrates of these interactions remain largely unknown. Here, we examined the role of the nociceptin/orphanin FQ (N/OFQ) system, with an animal model in which genetic selection for high alcohol preference has led to co-segregation of elevated behavioral sensitivity to stress (Marchigian Sardinian alcohol-preferring [msP]).
Methods: The msP and Wistar rats trained to self-administer alcohol received central injections of N/OFQ. In situ hybridization and receptor binding assays were also performed to evaluate N/OFQ receptor (NOP) function in naïve msP and Wistar rats.
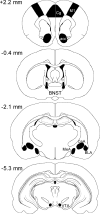
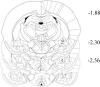
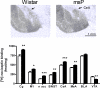
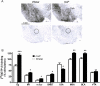
Results: Intracerebroventricular (ICV) injection of N/OFQ significantly inhibited alcohol self-administration in msP but not in nonselected Wistar rats. The NOP receptor messenger RNA expression and binding was upregulated across most brain regions in msP compared with Wistar rats. However, in msP rats [(35)S]GTPgammaS binding revealed a selective impairment of NOP receptor signaling in the central amygdala (CeA). Ethanol self-administration in msP rats was suppressed after N/OFQ microinjection into the CeA but not into the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis or the basolateral amygdala.
Conclusions: These findings indicate that dysregulation of N/OFQ-NOP receptor signaling in the CeA contributes to excessive alcohol intake in msP rats and that this phenotype can be rescued by local administration of pharmacological doses of exogenous N/OFQ. Data are interpreted on the basis of the anti-corticotropin releasing factor (CRF) actions of N/OFQ and the significance of the CRF system in promoting excessive alcohol drinking in msP rats.
Figures

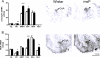
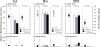
Similar articles
-
Dysregulation of Nociceptin/Orphanin FQ and Dynorphin Systems in the Extended Amygdala of Alcohol Preferring Marchigian Sardinian (msP) Rats.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 28;22(5):2448. doi: 10.3390/ijms22052448. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33671048 Free PMC article.
-
The biology of Nociceptin/Orphanin FQ (N/OFQ) related to obesity, stress, anxiety, mood, and drug dependence.Pharmacol Ther. 2014 Mar;141(3):283-99. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2013.10.011. Epub 2013 Nov 1. Pharmacol Ther. 2014. PMID: 24189487 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modification of anxiety-like behaviors by nociceptin/orphanin FQ (N/OFQ) and time-dependent changes in N/OFQ-NOP gene expression following ethanol withdrawal.Addict Biol. 2013 May;18(3):467-79. doi: 10.1111/j.1369-1600.2012.00466.x. Epub 2012 Jul 15. Addict Biol. 2013. PMID: 22804785 Free PMC article.
-
The nociceptin/orphanin FQ/NOP receptor system as a target for treatment of alcohol abuse: a review of recent work in alcohol-preferring rats.Physiol Behav. 2003 Jun;79(1):121-8. doi: 10.1016/s0031-9384(03)00112-4. Physiol Behav. 2003. PMID: 12818717
-
Nociceptin/orphanin FQ acts as a functional antagonist of corticotropin-releasing factor to inhibit its anorectic effect.Physiol Behav. 2004 Aug;82(1):63-8. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2004.04.035. Physiol Behav. 2004. PMID: 15234592 Review.
Cited by
-
Translational approach to develop novel medications on alcohol addiction: focus on neuropeptides.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2013 Aug;23(4):684-91. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2013.04.009. Epub 2013 May 3. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2013. PMID: 23648086 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Role for Neuropeptide S in Alcohol and Cocaine Seeking.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Jun 27;15(7):800. doi: 10.3390/ph15070800. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35890099 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of stimulation of mu opioid and nociceptin/orphanin FQ peptide (NOP) receptors on alcohol drinking in rhesus monkeys.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2019 Jul;44(8):1476-1484. doi: 10.1038/s41386-019-0390-z. Epub 2019 Apr 10. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2019. PMID: 30970376 Free PMC article.
-
Brain region-specific gene expression changes after chronic intermittent ethanol exposure and early withdrawal in C57BL/6J mice.Addict Biol. 2012 Mar;17(2):351-64. doi: 10.1111/j.1369-1600.2011.00357.x. Epub 2011 Aug 4. Addict Biol. 2012. PMID: 21812870 Free PMC article.
-
MT-7716, a potent NOP receptor agonist, preferentially reduces ethanol seeking and reinforcement in post-dependent rats.Addict Biol. 2015 Jul;20(4):643-51. doi: 10.1111/adb.12157. Epub 2014 Jun 16. Addict Biol. 2015. PMID: 24930632 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Meunier JC, Mollereau C, Toll L, Suaudeau C, Moisand C, Alvinerie P, Butour JL, Guillemot JC, Ferrara P, Monsarrat B, Mazarguil H, Vassart G, Parmentieer M, Costentin J. Isolation and structure of the endogenous agonist of opioid receptor- like ORL1 receptor. Nature. 1995;377:532–535. - PubMed
-
- Reinscheid RK, Nothacker HP, Bourson A, Ardati A, Henningsen RA, Bunzow JR, Grandy DK, Langen H, Monsma FJ, Jr, Civelli O. Orphanin FQ: neuropeptide that activates an opioidlike G protein-coupled receptor. Science. 1995;270:792–794. - PubMed
-
- Darland T, Heinricher MM, Grandy DK. Orphanin FQ/nociceptin: a role in pain and analgesia, but so much more. Trends Neurosci. 1998;21:215–221. - PubMed
-
- Mollereau C, Mouledous L. Tissue distribution of the opioid receptor-like (ORL1) receptor. Peptides. 2000;21:907–917. - PubMed
-
- Koob GF, Roberts AJ, Schulteis G, Parsons LH, Heyser CJ, Hyytia P, Merlo-Pich E, Weiss F. Neurocircuitry targets in ethanol reward and dependence. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1998;22:3–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

