CDC25A phosphatase controls meiosis I progression in mouse oocytes
- PMID: 18367163
- PMCID: PMC2430978
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2008.02.028
CDC25A phosphatase controls meiosis I progression in mouse oocytes
Abstract
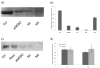
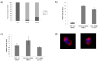
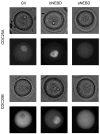
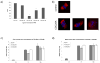
CDK1 is a pivotal regulator of resumption of meiosis and meiotic maturation of oocytes. CDC25A/B/C are dual-specificity phosphatases and activate cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs). Although CDC25C is not essential for either mitotic or meiotic cell cycle regulation, CDC25B is essential for CDK1 activation during resumption of meiosis. Cdc25a -/- mice are embryonic lethal and therefore a role for CDC25A in meiosis is unknown. We report that activation of CDK1 results in a maturation-associated decrease in the amount of CDC25A protein, but not Cdc25a mRNA, such that little CDC25A is present by metaphase I. In addition, expression of exogenous CDC25A overcomes cAMP-mediated maintenance of meiotic arrest. Microinjection of Gfp-Cdc25a and Gpf-Cdc25b mRNAs constructs reveals that CDC25A is exclusively localized to the nucleus prior to nuclear envelope breakdown (NEBD). In contrast, CDC25B localizes to cytoplasm in GV-intact oocytes and translocates to the nucleus shortly before NEBD. Over-expressing GFP-CDC25A, which compensates for the normal maturation-associated decrease in CDC25A, blocks meiotic maturation at MI. This MI block is characterized by defects in chromosome congression and spindle formation and a transient reduction in both CDK1 and MAPK activities. Lastly, RNAi-mediated reduction of CDC25A results in fewer oocytes resuming meiosis and reaching MII. These data demonstrate that CDC25A behaves differently during female meiosis than during mitosis, and moreover, that CDC25A has a function in resumption of meiosis, MI spindle formation and the MI-MII transition. Thus, both CDC25A and CDC25B are critical for meiotic maturation of oocytes.
Figures
References
-
- Baldin V, et al. Nuclear localization of CDC25B1 and serine 146 integrity are required for induction of mitosis. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:35176–82. - PubMed
-
- Baldin V, et al. PKB/Akt phosphorylates the CDC25B phosphatase and regulates its intracellular localisation. Biol Cell. 2003;95:547–54. - PubMed
-
- Cazales M, et al. CDC25B phosphorylation by Aurora-A occurs at the G2/M transition and is inhibited by DNA damage. Cell Cycle. 2005;4:1233–8. - PubMed
-
- Davezac N, et al. Regulation of CDC25B phosphatases subcellular localization. Oncogene. 2000;19:2179–85. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

