An Amsacta moorei entomopoxvirus ortholog of the poly(A) polymerase small subunit exhibits methyltransferase activity and is non-essential for virus growth
- PMID: 18367228
- PMCID: PMC2478561
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2008.02.023
An Amsacta moorei entomopoxvirus ortholog of the poly(A) polymerase small subunit exhibits methyltransferase activity and is non-essential for virus growth
Abstract
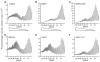
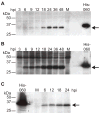
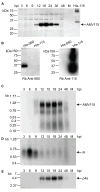
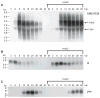
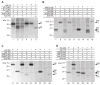
Unlike the heterodimeric poly(A) polymerase (PAP) of vaccinia virus (VACV), the PAP from the Amsacta moorei entomopoxvirus, AMEV, is potentially derived from three subunits: a single large and two small subunits (AMV060 and AMV115). The VACV small subunit serves as a 2'-O-methyltransferase, a processivity factor for mRNA polyadenylation, and a transcription elongation factor. We wished to determine the structure-function relationships of the three putative AMEV PAP subunits. We show that AMV060 is expressed as an early gene persisting throughout infection, whereas AMV115 is expressed late. We demonstrate that AMV060 exhibits 2'-O-methyltransferase activity but the gene is not essential for virus growth. Absence of the AMV060 protein has no effect on the length of the poly(A) tails present in mRNA. No physical association was found between any of the putative AMEV PAP subunits. We therefore propose that mRNA polyadenylation does not require interactions between these three proteins.
Figures

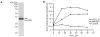
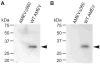
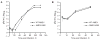
References
-
- Barbosa E, Moss B. mRNA(nucleoside-2′-)-methyltransferase from vaccinia virus. Purification and physical properties. J Biol Chem. 1978;253:7692–7697. - PubMed
-
- Bawden AL, Glassberg KJ, Diggans J, Shaw R, Farmerie W, Moyer RW. Complete genomic sequence of the Amsacta moorei entomopoxvirus: analysis and comparison with other poxviruses. Virology. 2000;274:120–139. - PubMed
-
- Becker MN, Moyer RW. Subfamily Entomopoxvirinae. In: Mercer A, Schmidt A, Weber O, editors. Poxviruses. Birkhäuser Publishing; Basel: 2007.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

