Intracellular delivery of an anionic antisense oligonucleotide via receptor-mediated endocytosis
- PMID: 18367474
- PMCID: PMC2377441
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkn115
Intracellular delivery of an anionic antisense oligonucleotide via receptor-mediated endocytosis
Abstract
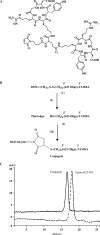
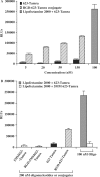
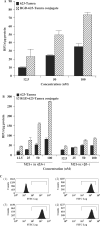
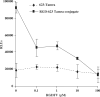
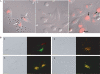
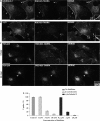
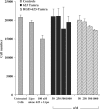
We describe the synthesis and characterization of a 5' conjugate between a 2'-O-Me phosphorothioate antisense oligonucleotide and a bivalent RGD (arginine-glycine-aspartic acid) peptide that is a high-affinity ligand for the alphavbeta3 integrin. We used alphavbeta3-positive melanoma cells transfected with a reporter comprised of the firefly luciferase gene interrupted by an abnormally spliced intron. Intranuclear delivery of a specific antisense oligonucleotide (termed 623) corrects splicing and allows luciferase expression in these cells. The RGD-623 conjugate or a cationic lipid-623 complex produced significant increases in luciferase expression, while 'free' 623 did not. However, the kinetics of luciferase expression was distinct; the RGD-623 conjugate produced a gradual increase followed by a gradual decline, while the cationic lipid-623 complex caused a rapid increase followed by a monotonic decline. The subcellular distribution of the oligonucleotide delivered using cationic lipids included both cytoplasmic vesicles and the nucleus, while the RGD-623 conjugate was primarily found in cytoplasmic vesicles that partially co-localized with a marker for caveolae. Both the cellular uptake and the biological effect of the RGD-623 conjugate were blocked by excess RGD peptide. These observations suggest that the bivalent RGD peptide-oligonucleotide conjugate enters cells via a process of receptor-mediated endocytosis mediated by the alphavbeta3 integrin.
Figures

References
-
- Kurreck J. Antisense technologies. Improvement through novel chemical modifications. Eur. J. Biochem. 2003;270:1628–1644. - PubMed
-
- Manoharan M. Oligonucleotide conjugates as potential antisense drugs with improved uptake, biodistribution, targeted delivery, and mechanism of action. Antisense Nucleic Acid Drug Dev. 2002;12:103–128. - PubMed
-
- Juliano RL, Yoo H. Aspects of the transport and delivery of antisense oligonucleotides. Curr. Opin. Mol. Ther. 2000;2:297–303. - PubMed
-
- Inoue A, Sawata SY, Taira K. Molecular design and delivery of siRNA. J. Drug. Target. 2006;14:448–455. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

