Recognition of tRNALeu by Aquifex aeolicus leucyl-tRNA synthetase during the aminoacylation and editing steps
- PMID: 18367476
- PMCID: PMC2377443
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkn028
Recognition of tRNALeu by Aquifex aeolicus leucyl-tRNA synthetase during the aminoacylation and editing steps
Abstract
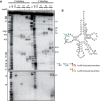
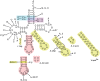
Recognition of tRNA by the cognate aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase during translation is crucial to ensure the correct expression of the genetic code. To understand tRNA(Leu) recognition sets and their evolution, the recognition of tRNA(Leu) by the leucyl-tRNA synthetase (LeuRS) from the primitive hyperthermophilic bacterium Aquifex aeolicus was studied by RNA probing and mutagenesis. The results show that the base A73; the core structure of tRNA formed by the tertiary interactions U8-A14, G18-U55 and G19-C56; and the orientation of the variable arm are critical elements for tRNA(Leu) aminoacylation. Although dispensable for aminoacylation, the anticodon arm carries discrete editing determinants that are required for stabilizing the conformation of the post-transfer editing state and for promoting translocation of the tRNA acceptor arm from the synthetic to the editing site.
Figures



References
-
- Watson JD, Hopkins NH, Roberts JW, Steitz JA, Weiner AM. Molecular Biology of the Gene, 4ed. Vol. 1. Menlo Park, CA: The Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Company; 1987.
-
- Chen JF, Guo NN, Li T, Wang ED, Wang YL. CP1 domain in Escherichia coli leucyl-tRNA synthetase is crucial for its editing function. Biochemistry. 2000;39:6726–6731. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

