The lack of anti-idiotypic antibodies, not the presence of the corresponding autoantibodies to glutamate decarboxylase, defines type 1 diabetes
- PMID: 18367670
- PMCID: PMC2291139
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0800578105
The lack of anti-idiotypic antibodies, not the presence of the corresponding autoantibodies to glutamate decarboxylase, defines type 1 diabetes
Abstract
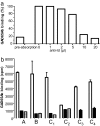
Autoantibodies to glutamate decarboxylase 65 (GAD65Ab) are commonly believed to be a major characteristic for type 1 diabetes (T1D). We investigated the presence of GAD65Ab in healthy individuals (n = 238) and first-degree relatives (FDRs) of T1D patients (n = 27) who tested negative for GAD65Ab in conventional RIAs. Sera were applied to affinity columns coated with GAD65-specific mAbs to absorb anti-idiotypic antibodies (anti-Ids). The absorbed sera were analyzed for binding to GAD65 by RIAs. Both healthy individuals and FDRs present GAD65Ab that are inhibited by anti-Id, masking them in conventional detection methods. The presence of GAD65Ab-specific anti-Ids was confirmed by competitive ELISA. Remarkably, T1D patients (n = 54) and Stiff Person Syndrome patients (n = 8) show a specific lack of anti-Ids to disease-associated GAD65Ab epitopes. Purified anti-Ids from healthy individuals and FDRs inhibited the binding of GAD65Ab from T1D patients to GAD65. We conclude that masked GAD65Ab are present in the healthy population and that a lack of particular anti-Ids, rather than GAD65Ab per se, is a characteristic of T1D. The lack of these inhibitory antibodies may contribute to T cell activation by GAD65Ab.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

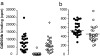
References
-
- Baekkeskov S, et al. Identification of the 64K autoantigen in insulin-dependent diabetes as the GABA-synthesizing enzyme glutamic acid decarboxylase. Nature. 1990;347:151–156. - PubMed
-
- Falorni A, Brozzetti A. Diabetes-related antibodies in adult diabetic patients. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005;19:119–133. - PubMed
-
- Falorni A, Laureti S, Santeusanio F. Autoantibodies in autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type II. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2002;31:369–389. - PubMed
-
- Solimena M, De Camilli P. Autoimmunity to glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) in Stiff Man syndrome and insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Trends Neurosci. 1991;14:452–457. - PubMed
-
- Verge CF, et al. Prediction of type I diabetes in first-degree relatives using a combination of insulin, GAD, and ICA512bdc/IA-2 autoantibodies. Diabetes. 1996;45:926–933. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

