Monte Carlo calculations and measurements of absorbed dose per monitor unit for the treatment of uveal melanoma with proton therapy
- PMID: 18367789
- PMCID: PMC4101899
- DOI: 10.1088/0031-9155/53/6/005
Monte Carlo calculations and measurements of absorbed dose per monitor unit for the treatment of uveal melanoma with proton therapy
Abstract
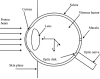
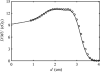
The treatment of uveal melanoma with proton radiotherapy has provided excellent clinical outcomes. However, contemporary treatment planning systems use simplistic dose algorithms that limit the accuracy of relative dose distributions. Further, absolute predictions of absorbed dose per monitor unit are not yet available in these systems. The purpose of this study was to determine if Monte Carlo methods could predict dose per monitor unit (D/MU) value at the center of a proton spread-out Bragg peak (SOBP) to within 1% on measured values for a variety of treatment fields relevant to ocular proton therapy. The MCNPX Monte Carlo transport code, in combination with realistic models for the ocular beam delivery apparatus and a water phantom, was used to calculate dose distributions and D/MU values, which were verified by the measurements. Measured proton beam data included central-axis depth dose profiles, relative cross-field profiles and absolute D/MU measurements under several combinations of beam penetration ranges and range-modulation widths. The Monte Carlo method predicted D/MU values that agreed with measurement to within 1% and dose profiles that agreed with measurement to within 3% of peak dose or within 0.5 mm distance-to-agreement. Lastly, a demonstration of the clinical utility of this technique included calculations of dose distributions and D/MU values in a realistic model of the human eye. It is possible to predict D/MU values accurately for clinical relevant range-modulated proton beams for ocular therapy using the Monte Carlo method. It is thus feasible to use the Monte Carlo method as a routine absolute dose algorithm for ocular proton therapy.
Figures






References
-
- Cascio EW, Sisterson J, Gottschalk B, Sarkar S. Measurements of the energy spectrum of degraded proton beams at NPTC Radiation Effects Data Workshop. IEEE; Piscataway, NJ: 2004.
-
- Constable IJ, Koehler AM. Experimental ocular irradiation with accelerated protons Invest. Ophthalmol. 1974;13:280–7. - PubMed
-
- Dobler B, Bendl R. Precise modelling of the eye for proton therapy of intra-ocular tumours. Phys. Med. Biol. 2002;47:593–613. - PubMed
-
- Egger E, Zografos L, Schalenbourg A, Beati D, Bohringer T, Chamot L, Goitein G. Eye retention after proton beam radiotherapy for uveal melanoma Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2003;55:867–80. - PubMed
-
- Goitein M, Miller T. Planning proton therapy of the eye. Med. Phys. 1983;10:275–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
