Sequence- and target-independent angiogenesis suppression by siRNA via TLR3
- PMID: 18368052
- PMCID: PMC2642938
- DOI: 10.1038/nature06765
Sequence- and target-independent angiogenesis suppression by siRNA via TLR3
Abstract
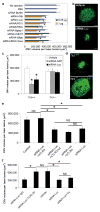
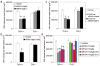
Clinical trials of small interfering RNA (siRNA) targeting vascular endothelial growth factor-A (VEGFA) or its receptor VEGFR1 (also called FLT1), in patients with blinding choroidal neovascularization (CNV) from age-related macular degeneration, are premised on gene silencing by means of intracellular RNA interference (RNAi). We show instead that CNV inhibition is a siRNA-class effect: 21-nucleotide or longer siRNAs targeting non-mammalian genes, non-expressed genes, non-genomic sequences, pro- and anti-angiogenic genes, and RNAi-incompetent siRNAs all suppressed CNV in mice comparably to siRNAs targeting Vegfa or Vegfr1 without off-target RNAi or interferon-alpha/beta activation. Non-targeted (against non-mammalian genes) and targeted (against Vegfa or Vegfr1) siRNA suppressed CNV via cell-surface toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3), its adaptor TRIF, and induction of interferon-gamma and interleukin-12. Non-targeted siRNA suppressed dermal neovascularization in mice as effectively as Vegfa siRNA. siRNA-induced inhibition of neovascularization required a minimum length of 21 nucleotides, a bridging necessity in a modelled 2:1 TLR3-RNA complex. Choroidal endothelial cells from people expressing the TLR3 coding variant 412FF were refractory to extracellular siRNA-induced cytotoxicity, facilitating individualized pharmacogenetic therapy. Multiple human endothelial cell types expressed surface TLR3, indicating that generic siRNAs might treat angiogenic disorders that affect 8% of the world's population, and that siRNAs might induce unanticipated vascular or immune effects.
Figures
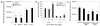
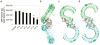
Comment in
-
RNA interference: generic block on angiogenesis.Nature. 2008 Apr 3;452(7187):543-5. doi: 10.1038/452543a. Nature. 2008. PMID: 18385725 No abstract available.
References
-
- Chiu YL, Ali A, Chu CY, Cao H, Rana TM. Visualizing a correlation between siRNA localization, cellular uptake, and RNAi in living cells. Chem Biol. 2004;11:1165–1175. - PubMed
-
- Soutschek J, et al. Therapeutic silencing of an endogenous gene by systemic administration of modified siRNAs. Nature. 2004;432:173–178. - PubMed
-
- Song E, et al. Antibody mediated in vivo delivery of small interfering RNAs via cellsurface receptors. Nature Biotechnol. 2005;23:709–717. - PubMed
-
- Reich SJ, et al. Small interfering RNA (siRNA) targeting VEGF effectively inhibits ocular neovascularization in a mouse model. Mol Vis. 2003;9:210–216. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

