P2 receptors in cardiovascular regulation and disease
- PMID: 18368530
- PMCID: PMC2245998
- DOI: 10.1007/s11302-007-9078-7
P2 receptors in cardiovascular regulation and disease
Abstract
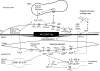
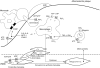
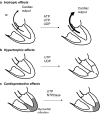
The role of ATP as an extracellular signalling molecule is now well established and evidence is accumulating that ATP and other nucleotides (ADP, UTP and UDP) play important roles in cardiovascular physiology and pathophysiology, acting via P2X (ion channel) and P2Y (G protein-coupled) receptors. In this article we consider the dual role of ATP in regulation of vascular tone, released as a cotransmitter from sympathetic nerves or released in the vascular lumen in response to changes in blood flow and hypoxia. Further, purinergic long-term trophic and inflammatory signalling is described in cell proliferation, differentiation, migration and death in angiogenesis, vascular remodelling, restenosis and atherosclerosis. The effects on haemostasis and cardiac regulation is reviewed. The involvement of ATP in vascular diseases such as thrombosis, hypertension and diabetes will also be discussed, as well as various heart conditions. The purinergic system may be of similar importance as the sympathetic and renin-angiotensin-aldosterone systems in cardiovascular regulation and pathophysiology. The extracellular nucleotides and their cardiovascular P2 receptors are now entering the phase of clinical development.
Figures

References
-
- Burnstock G (1978) A basis for distinguishing two types of purinergic receptor. In: Straub RW (ed) Cell membrane receptors for drugs and hormones: a multidisciplinary approach. Raven, New York, pp 107–118
-
- Burnstock G (1972) Purinergic nerves. Pharmacol Rev 24:509–581 - PubMed
-
- Burnstock G (1997) The past, present and future of purine nucleotides as signalling molecules. Neuropharmacology 36:1127–1139 - PubMed
-
- Ralevic V, Burnstock G (1998) Receptors for purines and pyrimidines. Pharmacol Rev 50:413–492 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

