Cardiac expression of Brn-3a and Brn-3b POU transcription factors and regulation of Hsp27 gene expression
- PMID: 18368538
- PMCID: PMC2673938
- DOI: 10.1007/s12192-008-0028-2
Cardiac expression of Brn-3a and Brn-3b POU transcription factors and regulation of Hsp27 gene expression
Abstract
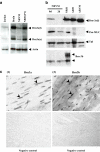
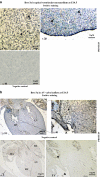
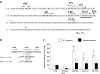
The Brn-3 family of transcription factors play a critical role in regulating expression of genes that control cell fate, including the small heat shock protein Hsp27. The aim of this study was to investigate the relationship between Brn-3a and Brn-3b and Hsp27 expression in the developing rodent heart. Brn-3a and Brn-3b were detected from embryonic days 9.5-10.5 (E9.5-E10.5) in the mouse heart, with significant increases seen later during development. Two isoforms (long and short) of each protein were detected during embryogenesis and postnatally. Brn-3a messenger RNA (mRNA) and protein were localized by E13.0 to the atrio-ventricular (AV) valve cushions and leaflets, outflow tract (OFT), epicardium and cardiac ganglia. By E14.5, Brn-3a was also localised to the septa and compact ventricular myocardium. An increase in expression of the long Brn-3a(l) isoform between E17 and adult coincided with a decrease in expression of Brn-3b(l) and a marked increase in expression of Hsp27. Hearts from Brn-3a-/- mice displayed a partially penetrant phenotype marked by thickening of the endocardial cushions and AV valve leaflets and hypoplastic ventricular myocardium. Loss of Brn-3a was correlated with a compensatory increase in Brn-3b and GATA3 mRNA but no change in Hsp27 mRNA. Reporter assays in isolated cardiomyocytes demonstrated that both Brn-3a and Brn-3b activate the hsp27 promoter via a consensus Brn-3-binding site. Therefore, Brn-3 POU factors may play an important role in the development and maintenance of critical cell types and structures within the heart, in part via developmental regulation of myocardial Hsp27 expression. Furthermore, Brn-3a may be necessary for correct valve and myocardial remodelling and maturation.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Essential but partially redundant roles for POU4F1/Brn-3a and POU4F2/Brn-3b transcription factors in the developing heart.Cell Death Dis. 2017 Jun 8;8(6):e2861. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2017.185. Cell Death Dis. 2017. PMID: 28594399 Free PMC article.
-
Co-expression of POU4F2/Brn-3b with p53 may be important for controlling expression of pro-apoptotic genes in cardiomyocytes following ischaemic/hypoxic insults.Cell Death Dis. 2014 Oct 30;5(10):e1503. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.452. Cell Death Dis. 2014. PMID: 25356872 Free PMC article.
-
Hsp-27 induction requires POU4F2/Brn-3b TF in doxorubicin-treated breast cancer cells, whereas phosphorylation alters its cellular localisation following drug treatment.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2011 Jul;16(4):427-39. doi: 10.1007/s12192-011-0256-8. Epub 2011 Jan 29. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2011. PMID: 21279488 Free PMC article.
-
Linking metabolic dysfunction with cardiovascular diseases: Brn-3b/POU4F2 transcription factor in cardiometabolic tissues in health and disease.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Mar 12;12(3):267. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-03551-9. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 33712567 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activation and repression of gene expression by POU family transcription factors.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1996 Apr 29;351(1339):511-5. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1996.0049. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1996. PMID: 8735273 Review.
Cited by
-
Brn3a regulates the transition from neurogenesis to terminal differentiation and represses non-neural gene expression in the trigeminal ganglion.Dev Dyn. 2009 Dec;238(12):3065-79. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.22145. Dev Dyn. 2009. PMID: 19877281 Free PMC article.
-
The POU4F2/Brn-3b transcription factor is required for the hypertrophic response to angiotensin II in the heart.Cell Death Dis. 2019 Aug 14;10(8):621. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1848-y. Cell Death Dis. 2019. PMID: 31413277 Free PMC article.
-
Essential but partially redundant roles for POU4F1/Brn-3a and POU4F2/Brn-3b transcription factors in the developing heart.Cell Death Dis. 2017 Jun 8;8(6):e2861. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2017.185. Cell Death Dis. 2017. PMID: 28594399 Free PMC article.
-
Co-expression of POU4F2/Brn-3b with p53 may be important for controlling expression of pro-apoptotic genes in cardiomyocytes following ischaemic/hypoxic insults.Cell Death Dis. 2014 Oct 30;5(10):e1503. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.452. Cell Death Dis. 2014. PMID: 25356872 Free PMC article.
-
Vascular dysfunction caused by loss of Brn-3b/POU4F2 transcription factor in aortic vascular smooth muscle cells is linked to deregulation of calcium signalling pathways.Cell Death Dis. 2023 Nov 25;14(11):770. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-06306-w. Cell Death Dis. 2023. PMID: 38007517 Free PMC article.
References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1007/BF00227734', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00227734'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '1471468', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1471468/'}]}
- Breitschopf H, Suchanek G, Gould RM, Colman DR, Lassmann H (1992) In situ hybridization with digoxigenin-labeled probes: sensitive and reliable detection method applied to myelinating rat brain. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 84:581–587 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1002/dvg.20340', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1002/dvg.20340'}, {'type': 'PMC', 'value': 'PMC2668208', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2668208/'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '17987658', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17987658/'}]}
- Brown DD, Christine KS, Showell C, Conlon FL (2007) Small heat shock protein Hsp27 is required for proper heart tube formation. Genesis 45:667–678 - PMC - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1074/jbc.270.6.2853', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.270.6.2853'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '7852360', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7852360/'}]}
- Budhram-Mahadeo V, Morris PJ, Lakin ND, Theil T, Ching GY, Lillycrop KA, Moroy T, Liem RK, Latchman DS (1995a) Activation of the alpha-internexin promoter by the Brn-3a transcription factor is dependent on the N-terminal region of the protein. J Biol Chem 270:2853–2858 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1016/0304-3940(94)11222-5', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-3940(94)11222-5'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '7731552', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7731552/'}]}
- Budhram-Mahadeo V, Lillycrop KA, Latchman DS (1995b) The levels of the antagonistic POU family transcription factors Brn-3a and Brn-3b in neuronal cells are regulated in opposite directions by serum growth factors. Neurosci Lett 185:48–51 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1038/sj.onc.1203072', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1203072'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '10597274', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10597274/'}]}
- Budhram-Mahadeo V, Ndisang D, Ward T, Weber BL, Latchman DS (1999a) The Brn-3b POU family transcription factor represses expression of the BRCA-1 anti-oncogene in breast cancer cells. Oncogene 18:6684–6691 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

