Crystallographic and biochemical studies revealing the structural basis for antizyme inhibitor function
- PMID: 18369191
- PMCID: PMC2327289
- DOI: 10.1110/ps.073427208
Crystallographic and biochemical studies revealing the structural basis for antizyme inhibitor function
Abstract
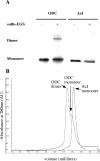
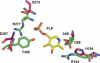
Antizyme inhibitor (AzI) regulates cellular polyamine homeostasis by binding to the polyamine-induced protein, Antizyme (Az), with greater affinity than ornithine decarboxylase (ODC). AzI is highly homologous to ODC but is not enzymatically active. In order to understand these specific characteristics of AzI and its differences from ODC, we determined the 3D structure of mouse AzI to 2.05 A resolution. Both AzI and ODC crystallize as a dimer. However, fewer interactions at the dimer interface, a smaller buried surface area, and lack of symmetry of the interactions between residues from the two monomers in the AzI structure suggest that this dimeric structure is nonphysiological. In addition, the absence of residues and interactions required for pyridoxal 5'-phosphate (PLP) binding suggests that AzI does not bind PLP. Biochemical studies confirmed the lack of PLP binding and revealed that AzI exists as a monomer in solution while ODC is dimeric. Our findings that AzI exists as a monomer and is unable to bind PLP provide two independent explanations for its lack of enzymatic activity and suggest the basis for its enhanced affinity toward Az.
Figures


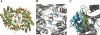


References
-
- Adams, E. Fluorometric determination of pyridoxal phosphate in enzymes. Methods Enzymol. 1979;62:407–410. - PubMed
-
- Almrud, J.J., Oliveira, M.A., Kern, A.D., Grishin, N.V., Phillips, M.A., Hackert, M.L. Crystal structure of human ornithine decarboxylase at 2.1 Å resolution: Structural insights to antizyme binding. J. Mol. Biol. 2000;295:7–16. - PubMed
-
- Bahadur, R.P., Chakrabarti, P., Rodier, F., Janin, J. A dissection of specific and non-specific protein–protein interfaces. J. Mol. Biol. 2004;336:943–955. - PubMed
-
- Bercovich, Z., Kahana, C. Degradation of antizyme inhibitor, an ornithine decarboxylase homologous protein, is ubiquitin-dependent and is inhibited by antizyme. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:54097–54102. - PubMed
-
- Boucek R.J., Jr, Lembach, K.J. Purification by affinity chromatography and preliminary characterization of ornithine decarboxylase from simian virus 40-transformed 3T3 mouse fibroblasts. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1977;184:408–415. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

