A novel mode of TRPML3 regulation by extracytosolic pH absent in the varitint-waddler phenotype
- PMID: 18369318
- PMCID: PMC2367400
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2008.56
A novel mode of TRPML3 regulation by extracytosolic pH absent in the varitint-waddler phenotype
Abstract
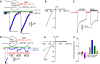
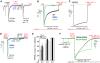
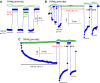
TRPML3 belongs to the TRPML subfamily of the transient receptor potential (TRP) channels. The A419P mutation in TRPML3 causes the varitint-waddler phenotype as a result of gain-of-function mutation (GOF). Regulation of the channels and the mechanism by which the A419P mutation leads to GOF are not known. We report here that TRPML3 is a Ca(2+)-permeable channel with a unique form of regulation by extracytosolic (luminal) H(+) (H(+)(e-cyto)). Regulation by H(+)(e-cyto) is mediated by a string of three histidines (H252, H273, H283) in the large extracytosolic loop between transmembrane domains (TMD) 1 and 2. Each of the histidines has a unique role, whereby H252 and H273 retard access of H(+)(e-cyto) to the inhibitory H283. Notably, the H283A mutation has the same phenotype as A419P and locks the channel in an open state, whereas the H283R mutation inactivates the channel. Accordingly, A419P eliminates regulation of TRPML3 by H(+)(e-cyto), and confers full activation to TRPML3(H283R). Activation of TRPML3 and regulation by H(+)(e-cyto) are altered by both the alpha-helix-destabilizing A419G and the alpha-helix-favouring A419M and A419K. These findings suggest that regulation of TRPML3 by H(+)(e-cyto) is due to an effect of the large extracytosolic loop on the orientation of fifth TMD and thus pore opening and show that the GOF of TRPML3(A419P) is due to disruption of this communication.
Figures



References
-
- Bargal R, Avidan N, Ben-Asher E, Olender Z, Zeigler M, Frumkin A, Raas-Rothschild A, Glusman G, Lancet D, Bach G (2000) Identification of the gene causing mucolipidosis type IV. Nat Genet 26: 118–123 - PubMed
-
- Cable J, Steel KP (1998) Combined cochleo-saccular and neuroepithelial abnormalities in the Varitint-waddler-J (VaJ) mouse. Hear Res 123: 125–136 - PubMed
-
- den Dekker E, Hoenderop JG, Nilius B, Bindels RJ (2003) The epithelial calcium channels, TRPV5 & TRPV6: from identification towards regulation. Cell Calcium 33: 497–507 - PubMed
-
- Fares H, Greenwald I (2001) Regulation of endocytosis by CUP-5, the Caenorhabditis elegans mucolipin-1 homolog. Nat Genet 28: 64–68 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

