Transcription and chromatin organization of a housekeeping gene cluster containing an integrated beta-globin locus control region
- PMID: 18369441
- PMCID: PMC2265466
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000016
Transcription and chromatin organization of a housekeeping gene cluster containing an integrated beta-globin locus control region
Erratum in
- PLoS Genet. 2008 Mar;4(3). doi: 10.1371/annotation/b4241c5d-5403-4797-8579-913ef9be560b. Pombo, Ana [added]
Abstract
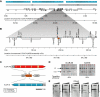
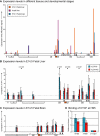
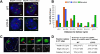
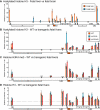
The activity of locus control regions (LCR) has been correlated with chromatin decondensation, spreading of active chromatin marks, locus repositioning away from its chromosome territory (CT), increased association with transcription factories, and long-range interactions via chromatin looping. To investigate the relative importance of these events in the regulation of gene expression, we targeted the human beta-globin LCR in two opposite orientations to a gene-dense region in the mouse genome containing mostly housekeeping genes. We found that each oppositely oriented LCR influenced gene expression on both sides of the integration site and over a maximum distance of 150 kilobases. A subset of genes was transcriptionally enhanced, some of which in an LCR orientation-dependent manner. The locus resides mostly at the edge of its CT and integration of the LCR in either orientation caused a more frequent positioning of the locus away from its CT. Locus association with transcription factories increased moderately, both for loci at the edge and outside of the CT. These results show that nuclear repositioning is not sufficient to increase transcription of any given gene in this region. We identified long-range interactions between the LCR and two upregulated genes and propose that LCR-gene contacts via chromatin looping determine which genes are transcriptionally enhanced.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Epner E, Reik A, Cimbora D, Telling A, Bender MA, et al. The beta-globin LCR is not necessary for an open chromatin structure or developmentally regulated transcription of the native mouse beta-globin locus. Mol Cell. 1998;2:447–455. - PubMed
-
- Grosveld F, van Assendelft GB, Greaves DR, Kollias G. Position-independent, high-level expression of the human beta-globin gene in transgenic mice. Cell. 1987;51:975–985. - PubMed
-
- Ho Y, Elefant F, Cooke N, Liebhaber S. A defined locus control region determinant links chromatin domain acetylation with long-range gene activation. Mol Cell. 2002;9:291–302. - PubMed
-
- Routledge SJ, Proudfoot NJ. Definition of transcriptional promoters in the human beta globin locus control region. J Mol Biol. 2002;323:601–611. - PubMed
-
- Ling J, Ainol L, Zhang L, Yu X, Pi W, et al. HS2 enhancer function is blocked by a transcriptional terminator inserted between the enhancer and the promoter. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:51704–51713. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

