Structural biology of proline catabolism
- PMID: 18369526
- PMCID: PMC2664619
- DOI: 10.1007/s00726-008-0062-5
Structural biology of proline catabolism
Abstract
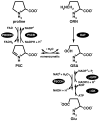
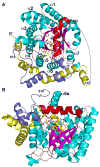
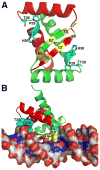
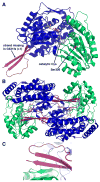
The proline catabolic enzymes proline dehydrogenase and Delta(1)-pyrroline-5-carboxylate dehydrogenase catalyze the 4-electron oxidation of proline to glutamate. These enzymes play important roles in cellular redox control, superoxide generation, apoptosis and cancer. In some bacteria, the two enzymes are fused into the bifunctional enzyme, proline utilization A. Here we review the three-dimensional structural information that is currently available for proline catabolic enzymes. Crystal structures have been determined for bacterial monofunctional proline dehydrogenase and Delta(1)-pyrroline-5-carboxylate dehydrogenase, as well as the proline dehydrogenase and DNA-binding domains of proline utilization A. Some of the functional insights provided by analyses of these structures are discussed, including substrate recognition, catalytic mechanism, biochemical basis of inherited proline catabolic disorders and DNA recognition by proline utilization A.
Figures




References
-
- Adams E, Frank L. Metabolism of proline and the hydroxyprolines. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:1005–1061. - PubMed
-
- Baban BA, Vinod MP, Tanner JJ, Becker DF. Probing a hydrogen bond pair and the FAD redox properties in the proline dehydrogenase domain of Escherichia coli PutA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004;1701:49–59. - PubMed
-
- Bearne SL, Wolfenden R. Glutamate gamma-semialdehyde as a natural transition state analogue inhibitor of Escherichia coli glucosamine-6-phosphate synthase. Biochemistry. 1995;34:11515–11520. - PubMed
-
- Becker DF, Thomas EA. Redox properties of the PutA protein from Escherichia coli and the influence of the flavin redox state on PutA-DNA interactions. Biochemistry. 2001;40:4714–4721. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

