The development of germline stem cells in Drosophila
- PMID: 18370048
- PMCID: PMC2729445
- DOI: 10.1007/978-1-60327-214-8_1
The development of germline stem cells in Drosophila
Abstract
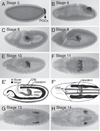
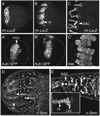
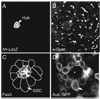
Germline stem cells (GSCs) in Drosophila are a valuable model to explore of how adult stem cells are regulated in vivo. Genetic dissection of this system has shown that stem cell fate is determined and maintained by the stem cell's somatic microenvironment or niche. In Drosophila gonads, the stem cell niche -- the cap cell cluster in females and the hub in males -- acts as a signaling center to recruit GSCs from among a small population of undifferentiated primordial germ cells (PGCs). Short-range signals from the niche specify and regulate stem cell fate by maintaining the undifferentiated state of the PGCs next to the niche. Germline cells that do not receive the niche signals because of their location assume the default fate and differentiate. Once GSCs are specified, adherens junctions maintain close association between the stem cells and their niche and help to orient stem cell division so that one daughter is displaced from the niche and differentiates. In females, stem cell fate depends on bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) signals from the cap cells; in males, hub cells express the cytokine-like ligand Unpaired, which activates the Janus kinase-signal transducers and activators of transcription (Jak-Stat) pathway in stem cells. Although the signaling pathways operating between the niche and stem cells are different, there are common general features in both males and females, including the arrangement of cell types, many of the genes used, and the logic of the system that maintains stem cell fate.
Figures
References
-
- Fuchs E, Tumbar T, Guasch G. Socializing with the neighbors: stem cells and their niche. Cell. 2004;116:769–778. - PubMed
-
- Wong MD, Jin Z, Xie T. Molecular mechanisms of germline stem cell regulation. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2005;39:173–195. - PubMed
-
- Mahowald AP. Assembly of the Drosophila germ plasm. Int. Rev. Cytol. 2001;203:187–213. - PubMed
-
- Seydoux G, Schedl T. The germline in C. elegans: origins, proliferation, and silencing. Int. Rev. Cytol. 2001;203:139–185. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

