Improved production of human type II procollagen in the yeast Pichia pastoris in shake flasks by a wireless-controlled fed-batch system
- PMID: 18371201
- PMCID: PMC2315644
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6750-8-33
Improved production of human type II procollagen in the yeast Pichia pastoris in shake flasks by a wireless-controlled fed-batch system
Abstract
Background: Here we describe a new technical solution for optimization of Pichia pastoris shake flask cultures with the example of production of stable human type II collagen. Production of recombinant proteins in P. pastoris is usually performed by controlling gene expression with the strong AOX1 promoter, which is induced by addition of methanol. Optimization of processes using the AOX1 promoter in P. pastoris is generally done in bioreactors by fed-batch fermentation with a controlled continuous addition of methanol for avoiding methanol toxification and carbon/energy starvation. The development of feeding protocols and the study of AOX1-controlled recombinant protein production have been largely made in shake flasks, although shake flasks have very limited possibilities for measurement and control.
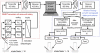
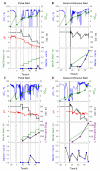
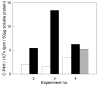
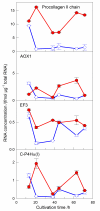
Results: By applying on-line pO2 monitoring we demonstrate that the widely used pulse feeding of methanol results in long phases of methanol exhaustion and consequently low expression of AOX1 controlled genes. Furthermore, we provide a solution to apply the fed-batch strategy in shake flasks. The presented solution applies a wireless feeding unit which can be flexibly positioned and allows the use of computer-controlled feeding profiles. By using the human collagen II as an example we show that a quasi-continuous feeding profile, being the simplest way of a fed-batch fermentation, results in a higher production level of human collagen II. Moreover, the product has a higher proteolytic stability compared to control cultures due to the increased expression of human collagen prolyl 4-hydroxylase as monitored by mRNA and protein levels.
Conclusion: The recommended standard protocol for methanol addition in shake flasks using pulse feeding is non-optimal and leads to repeated long phases of methanol starvation. The problem can be solved by applying the fed-batch technology. The presented wireless feeding unit, together with an on-line monitoring system offers a flexible, simple, and low-cost solution for initial optimization of the production in shake flasks which can be performed in parallel. By this way the fed-batch strategy can be applied from the early screening steps also in laboratories which do not have access to high-cost and complicated bioreactor systems.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Enhancement of thermoalkaliphilic xylanase production by Pichia pastoris through novel fed-batch strategy in high cell-density fermentation.BMC Biotechnol. 2017 Jun 21;17(1):55. doi: 10.1186/s12896-017-0361-6. BMC Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 28633643 Free PMC article.
-
A new wireless system for decentralised measurement of physiological parameters from shake flasks.Microb Cell Fact. 2006 Feb 24;5:8. doi: 10.1186/1475-2859-5-8. Microb Cell Fact. 2006. PMID: 16504107 Free PMC article.
-
Functional recombinant protein is present in the pre-induction phases of Pichia pastoris cultures when grown in bioreactors, but not shake-flasks.Microb Cell Fact. 2014 Sep 4;13(1):127. doi: 10.1186/s12934-014-0127-y. Microb Cell Fact. 2014. PMID: 25186468 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering strategies for enhanced production of protein and bio-products in Pichia pastoris: A review.Biotechnol Adv. 2018 Jan-Feb;36(1):182-195. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2017.11.002. Epub 2017 Nov 10. Biotechnol Adv. 2018. PMID: 29129652 Review.
-
Fed-batch high-cell-density fermentation strategies for Pichia pastoris growth and production.Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2019 Mar;39(2):258-271. doi: 10.1080/07388551.2018.1554620. Epub 2019 Jan 2. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 30599783 Review.
Cited by
-
Development of a circulation direct sampling and monitoring system for O2 and CO2 concentrations in the gas-liquid phases of shake-flask systems during microbial cell culture.AMB Express. 2017 Aug 23;7(1):163. doi: 10.1186/s13568-017-0464-4. AMB Express. 2017. PMID: 28831757 Free PMC article.
-
Enzyme controlled glucose auto-delivery for high cell density cultivations in microplates and shake flasks.Microb Cell Fact. 2008 Nov 18;7:31. doi: 10.1186/1475-2859-7-31. Microb Cell Fact. 2008. PMID: 19017379 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive clone screening and evaluation of fed-batch strategies in a microbioreactor and lab scale stirred tank bioreactor system: application on Pichia pastoris producing Rhizopus oryzae lipase.Microb Cell Fact. 2014 Mar 7;13(1):36. doi: 10.1186/1475-2859-13-36. Microb Cell Fact. 2014. PMID: 24606982 Free PMC article.
-
Sandwich hybridization assay for sensitive detection of dynamic changes in mRNA transcript levels in crude Escherichia coli cell extracts in response to copper ions.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2008 Dec;74(24):7463-70. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01370-08. Epub 2008 Oct 24. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18952865 Free PMC article.
-
Easy to use and reliable technique for online dissolved oxygen tension measurement in shake flasks using infrared fluorescent oxygen-sensitive nanoparticles.Microb Cell Fact. 2016 Feb 24;15:45. doi: 10.1186/s12934-016-0444-4. Microb Cell Fact. 2016. PMID: 26912130 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cereghino GP, Sunga AJ, Cereghino JL, Cregg JM. Expression of foreign genes in the yeast Pichia pastoris. Genet Eng (N Y ) 2001;23:157–169. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

