Sequential expression of pluripotency markers during direct reprogramming of mouse somatic cells
- PMID: 18371436
- PMCID: PMC2276627
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2008.01.004
Sequential expression of pluripotency markers during direct reprogramming of mouse somatic cells
Abstract
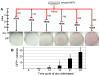
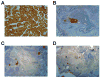
Pluripotency can be induced in differentiated murine and human cells by retroviral transduction of Oct4, Sox2, Klf4, and c-Myc. We have devised a reprogramming strategy in which these four transcription factors are expressed from doxycycline (dox)-inducible lentiviral vectors. Using these inducible constructs, we derived induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells from mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) and found that transgene silencing is a prerequisite for normal cell differentiation. We have analyzed the timing of known pluripotency marker activation during mouse iPS cell derivation and observed that alkaline phosphatase (AP) was activated first, followed by stage-specific embryonic antigen 1 (SSEA1). Expression of Nanog and the endogenous Oct4 gene, marking fully reprogrammed cells, was only observed late in the process. Importantly, the virally transduced cDNAs needed to be expressed for at least 12 days in order to generate iPS cells. Our results are a step toward understanding some of the molecular events governing epigenetic reprogramming.
Figures
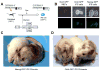
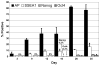
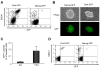
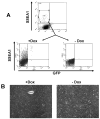

References
-
- Alberti S, Parks DR, Herzenberg LA. A single laser method for subtraction of cell autofluorescence in flow cytometry. Cytometry. 1987;8:114–119. - PubMed
-
- Beard C, Hochedlinger K, Plath K, Wutz A, Jaenisch R. Efficient method to generate single-copy transgenic mice by site-specific integration in embryonic stem cells. Genesis. 2006;44:23–28. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein BE, Mikkelsen TS, Xie X, Kamal M, Huebert DJ, Cuff J, Fry B, Meissner A, Wernig M, Plath K, et al. A bivalent chromatin structure marks key developmental genes in embryonic stem cells. Cell. 2006;125:315–326. - PubMed
-
- Cowan CA, Atienza J, Melton DA, Eggan K. Nuclear reprogramming of somatic cells after fusion with human embryonic stem cells. Science. 2005;309:1369–1373. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

