Dopamine D4 receptors regulate intracellular calcium concentration in cultured chicken cone photoreceptor cells: relationship to dopamine receptor-mediated inhibition of cAMP formation
- PMID: 18371938
- PMCID: PMC2480521
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2008.02.025
Dopamine D4 receptors regulate intracellular calcium concentration in cultured chicken cone photoreceptor cells: relationship to dopamine receptor-mediated inhibition of cAMP formation
Abstract
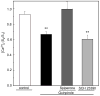
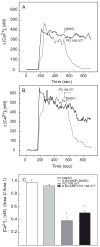
Dopamine is a retinal neuromodulator secreted from amacrine and interplexiform cells. Activation of dopamine D4 receptors on photoreceptor cells reduces a light-sensitive pool of cAMP. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the role of dopamine receptors and cAMP in the regulation of intracellular Ca(2+) concentrations ([Ca(2+)](i)) in photoreceptor cells of chick retina. Retinal cells from 6 day-old chicken embryos were isolated and cultured for 5-7 days prior to experiments. Cone photoreceptors were the predominant cell type in these cultures. Dopamine and agonists of dopamine D4 receptors suppressed K(+)-stimulated uptake of (45)Ca(2+) and [Ca(2+)](i), measured with the Ca(2+)-sensitive fluorescent dye fura-2AM. The effects of the agonists were blocked by dopamine D2/D4 receptor antagonists or by pertussis toxin. 8Br-cAMP, a cell-permeable analog of cAMP, had no effect on inhibition of K(+)-stimulated (45)Ca(2+) influx or [Ca(2+)](i) by dopamine D2/D4 receptor agonists. Quinpirole inhibited the increase in cAMP level elicited by K(+), which requires Ca(2+) influx through voltage-gated Ca(2+) channels, but not that induced by the calcium ionophore A23187. Moreover, dopamine had no effect on either forskolin-stimulated or Ca(2+)/calmodulin-stimulated adenylyl cyclase activity in cell membranes prepared from the cultured cells. These data indicate that the decrease of cAMP elicited by dopamine D4 receptor stimulation may be secondary to decreased [Ca(2+)](i).
Figures
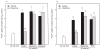




Similar articles
-
Cloning, expression, functional coupling and pharmacological characterization of the rat dopamine D4 receptor.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2000 May;361(5):555-64. doi: 10.1007/s002100000236. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 10832611
-
Pharmacological and functional characterisation of dopamine D4 receptors in the rat retina.Neuropharmacology. 2003 Jun;44(8):1038-46. doi: 10.1016/s0028-3908(03)00112-6. Neuropharmacology. 2003. PMID: 12763097
-
Dysfunctional light-evoked regulation of cAMP in photoreceptors and abnormal retinal adaptation in mice lacking dopamine D4 receptors.J Neurosci. 2002 Mar 15;22(6):2063-73. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-06-02063.2002. J Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 11896146 Free PMC article.
-
Dopamine D4-like receptors in vertebrate retina: does the retina offer a model for the D4-receptor analysis?Pol J Pharmacol. 1997 Aug;49(4):201-11. Pol J Pharmacol. 1997. PMID: 9437763 Review.
-
Retinal dopamine D1 and D2 receptors: characterization by binding or pharmacological studies and physiological functions.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 1990 Sep;10(3):303-25. doi: 10.1007/BF00711177. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 1990. PMID: 2174740 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Impaired Light Adaptation of ON-Sustained Ganglion Cells in Early Diabetes Is Attributable to Diminished Response to Dopamine D4 Receptor Activation.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2022 Jan 3;63(1):33. doi: 10.1167/iovs.63.1.33. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2022. PMID: 35077550 Free PMC article.
-
The Role and Therapeutic Potential of Melatonin in Degenerative Fundus Diseases: Diabetes Retinopathy and Age-Related Macular Degeneration.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024 Jun 18;18:2329-2346. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S471525. eCollection 2024. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024. PMID: 38911030 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mislocalized opsin and cAMP signaling: a mechanism for sprouting by rod cells in retinal degeneration.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012 Sep 19;53(10):6355-69. doi: 10.1167/iovs.12-10180. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012. PMID: 22899763 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of dopamine signaling suppresses cGMP accumulation in rd1 retinal organ cultures.Neuroreport. 2014 May 28;25(8):601-6. doi: 10.1097/WNR.0000000000000145. Neuroreport. 2014. PMID: 24614363 Free PMC article.
-
Role of dopamine in distal retina.J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol. 2014 May;200(5):333-58. doi: 10.1007/s00359-014-0906-2. Epub 2014 Apr 12. J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24728309 Review.
References
-
- Akopian A, Witkovsky P. D2 dopamine receptor-mediated inhibition of a hyperpolarization-activated current in rod photoreceptors. J Neurophysiol. 1996;76:1828–1835. - PubMed
-
- Alonso-Gómez AL, Iuvone PM. Melatonin biosynthesis in cultured chick retinal photoreceptor cells: calcium and cyclic AMP protect serotonin N-acetyltransferase from inactivation in cycloheximide-treated cells. J Neurochem. 1995;65:1054–1060. - PubMed
-
- Avendano G, Butler BJ, Iuvone PM. K+- Evoked depolarization incceases serotonin N-acetyltransferase activity in photoreceptor-enriched retinal cell cultures. Involvement of calcium influx through L-type calcium channels. Neurochem Int. 1990;17:117–126. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

