Reaction mechanism and structural model of ADP-forming Acetyl-CoA synthetase from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus: evidence for a second active site histidine residue
- PMID: 18372246
- PMCID: PMC3258870
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M710218200
Reaction mechanism and structural model of ADP-forming Acetyl-CoA synthetase from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus: evidence for a second active site histidine residue
Abstract
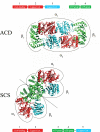
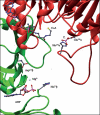
In Archaea, acetate formation and ATP synthesis from acetyl-CoA is catalyzed by an unusual ADP-forming acetyl-CoA synthetase (ACD) (acetyl-CoA + ADP + P(i) acetate + ATP + HS-CoA) catalyzing the formation of acetate from acetyl-CoA and concomitant ATP synthesis by the mechanism of substrate level phosphorylation. ACD belongs to the protein superfamily of nucleoside diphosphate-forming acyl-CoA synthetases, which also include succinyl-CoA synthetases (SCSs). ACD differs from SCS in domain organization of subunits and in the presence of a second highly conserved histidine residue in the beta-subunit, which is absent in SCS. The influence of these differences on structure and reaction mechanism of ACD was studied with heterotetrameric ACD (alpha(2)beta(2)) from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus in comparison with heterotetrameric SCS. A structural model of P. furiosus ACD was constructed suggesting a novel spatial arrangement of the subunits different from SCS, however, maintaining a similar catalytic site. Furthermore, kinetic and molecular properties and enzyme phosphorylation as well as the ability to catalyze arsenolysis of acetyl-CoA were studied in wild type ACD and several mutant enzymes. The data indicate that the formation of enzyme-bound acetyl phosphate and enzyme phosphorylation at His-257alpha, respectively, proceed in analogy to SCS. In contrast to SCS, in ACD the phosphoryl group is transferred from the His-257alpha to ADP via transient phosphorylation of a second conserved histidine residue in the beta-subunit, His-71beta. It is proposed that ACD reaction follows a novel four-step mechanism including transient phosphorylation of two active site histidine residues:
Figures

Similar articles
-
Acetyl coenzyme A synthetase (ADP forming) from the hyperthermophilic Archaeon pyrococcus furiosus: identification, cloning, separate expression of the encoding genes, acdAI and acdBI, in Escherichia coli, and in vitro reconstitution of the active heterotetrameric enzyme from its recombinant subunits.J Bacteriol. 1999 Sep;181(18):5885-8. doi: 10.1128/JB.181.18.5885-5888.1999. J Bacteriol. 1999. PMID: 10482538 Free PMC article.
-
Novel type of ADP-forming acetyl coenzyme A synthetase in hyperthermophilic archaea: heterologous expression and characterization of isoenzymes from the sulfate reducer Archaeoglobus fulgidus and the methanogen Methanococcus jannaschii.J Bacteriol. 2002 Feb;184(3):636-44. doi: 10.1128/JB.184.3.636-644.2002. J Bacteriol. 2002. PMID: 11790732 Free PMC article.
-
A novel ADP-forming succinyl-CoA synthetase in Thermococcus kodakaraensis structurally related to the archaeal nucleoside diphosphate-forming acetyl-CoA synthetases.J Biol Chem. 2007 Sep 14;282(37):26963-26970. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M702694200. Epub 2007 Jul 19. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17640871
-
Investigating the mechanism of ADP-forming acetyl-CoA synthetase from the protozoan parasite Entamoeba histolytica.FEBS Lett. 2017 Feb;591(4):603-612. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.12573. Epub 2017 Feb 9. FEBS Lett. 2017. PMID: 28129670 Free PMC article.
-
Conformational dynamics in the Acyl-CoA synthetases, adenylation domains of non-ribosomal peptide synthetases, and firefly luciferase.ACS Chem Biol. 2009 Oct 16;4(10):811-27. doi: 10.1021/cb900156h. ACS Chem Biol. 2009. PMID: 19610673 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genome sequencing of a single cell of the widely distributed marine subsurface Dehalococcoidia, phylum Chloroflexi.ISME J. 2014 Feb;8(2):383-97. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2013.143. Epub 2013 Aug 22. ISME J. 2014. PMID: 23966099 Free PMC article.
-
Methanotrophic archaea possessing diverging methane-oxidizing and electron-transporting pathways.ISME J. 2014 May;8(5):1069-78. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2013.212. Epub 2013 Dec 12. ISME J. 2014. PMID: 24335827 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of two members among the five ADP-forming acyl coenzyme A (Acyl-CoA) synthetases reveals the presence of a 2-(Imidazol-4-yl)acetyl-CoA synthetase in Thermococcus kodakarensis.J Bacteriol. 2014 Jan;196(1):140-7. doi: 10.1128/JB.00877-13. Epub 2013 Oct 25. J Bacteriol. 2014. PMID: 24163338 Free PMC article.
-
Acetyl Phosphate as a Primordial Energy Currency at the Origin of Life.Orig Life Evol Biosph. 2018 Jun;48(2):159-179. doi: 10.1007/s11084-018-9555-8. Epub 2018 Mar 3. Orig Life Evol Biosph. 2018. PMID: 29502283 Free PMC article.
-
Single-Cell Genomics Reveals a Diverse Metabolic Potential of Uncultivated Desulfatiglans-Related Deltaproteobacteria Widely Distributed in Marine Sediment.Front Microbiol. 2018 Sep 3;9:2038. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02038. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30233524 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Reeves, R. E., Warren, L. G., Susskind, B., and Lo, H. S. (1977) J. Biol. Chem. 252 726-731 - PubMed
-
- Sanchez, L. B., and Müller, M. (1996) FEBS Lett. 378 240-244 - PubMed
-
- Schäfer, T., Selig, M., and Schönheit, P. (1993) Arch. Microbiol. 159 72-83
-
- Schönheit, P., and Schäfer, T. (1995) World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 11 26-57 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

