Predicting the FSH threshold dose in women with WHO Group II anovulatory infertility failing to ovulate or conceive on clomiphene citrate
- PMID: 18372254
- PMCID: PMC2387217
- DOI: 10.1093/humrep/den089
Predicting the FSH threshold dose in women with WHO Group II anovulatory infertility failing to ovulate or conceive on clomiphene citrate
Abstract
BACKGROUND The objective of this investigation was to establish independent predictors of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) threshold dose in anovulatory women undergoing ovulation induction with FSH preparations.
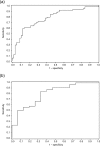
Methods: One hundred and fifty-one patients with WHO Group II anovulatory infertility failing to ovulate or conceive on clomiphene citrate underwent ovarian stimulation with FSH-only preparations following a low-dose step-up protocol. The individual FSH threshold dose was defined as the FSH dose when meeting the human chorionic gonadotrophin criteria (one follicle > or =17 mm, or 2-3 follicles > or =15 mm). The influence of demographics, physical characteristics, obstetric and infertility and menstrual cycle history, ovarian ultrasonography, endocrine parameters and type of gonadotrophin preparation on the FSH threshold dose was assessed through multiple regression analysis.
Results: In the univariate analysis, age, body mass index (BMI), failure to ovulate with clomiphene citrate, menstrual cycle history (amenorrhea, oligomenorrhea or anovulatory cycles of 21-35 days), mean ovarian volume, LH/FSH ratio, testosterone and free androgen index were significant (P < 0.05) predictors of FSH threshold dose. In the multivariate analysis, menstrual cycle history, mean ovarian volume and BMI remained significant (P < 0.001).
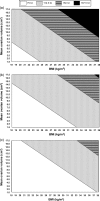
Conclusions: The individual FSH threshold dose for ovulation induction in anovulatory women can be predicted based on three variables easily determined in clinical practice: menstrual cycle history, mean ovarian volume and BMI. A FSH dosage nomogram was constructed based on these parameters.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Predictors of patients remaining anovulatory during clomiphene citrate induction of ovulation in normogonadotropic oligoamenorrheic infertility.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1998 Jul;83(7):2361-5. doi: 10.1210/jcem.83.7.4919. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1998. PMID: 9661609 Clinical Trial.
-
Free androgen index and leptin are the most prominent endocrine predictors of ovarian response during clomiphene citrate induction of ovulation in normogonadotropic oligoamenorrheic infertility.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2000 Feb;85(2):676-82. doi: 10.1210/jcem.85.2.6356. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2000. PMID: 10690875
-
Ovulation induction in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: randomized trial of clomiphene citrate versus low-dose recombinant FSH as first line therapy.Reprod Biomed Online. 2004 Oct;9(4):382-90. doi: 10.1016/s1472-6483(10)61273-4. Reprod Biomed Online. 2004. PMID: 15511336 Clinical Trial.
-
Modern use of clomiphene citrate in induction of ovulation.Hum Reprod Update. 1997 Jul-Aug;3(4):359-65. doi: 10.1093/humupd/3.4.359. Hum Reprod Update. 1997. PMID: 9459281 Review.
-
Low-dose FSH therapy for anovulatory infertility associated with polycystic ovary syndrome: rationale, results, reflections and refinements.Hum Reprod Update. 1999 Sep-Oct;5(5):493-9. doi: 10.1093/humupd/5.5.493. Hum Reprod Update. 1999. PMID: 10582786 Review.
Cited by
-
Obesity and Polycystic Ovary Syndrome.J Obes Metab Syndr. 2024 Dec 30;33(4):289-301. doi: 10.7570/jomes24035. Epub 2024 Dec 20. J Obes Metab Syndr. 2024. PMID: 39701598 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phenotyping male infertility in the mouse: how to get the most out of a 'non-performer'.Hum Reprod Update. 2010 Mar-Apr;16(2):205-24. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmp032. Epub 2009 Sep 15. Hum Reprod Update. 2010. PMID: 19758979 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ovulation induction with minimal dose of follitropin alfa: a case series study.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2011 Oct 24;9:142. doi: 10.1186/1477-7827-9-142. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2011. PMID: 22024419 Free PMC article.
-
Phase IV, open-label, randomized study of low-dose recombinant human follicle-stimulating hormone protocols for ovulation induction.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2014 Jun 18;12:52. doi: 10.1186/1477-7827-12-52. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2014. PMID: 24942155 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Diagnosis and treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013 Dec;98(12):4565-92. doi: 10.1210/jc.2013-2350. Epub 2013 Oct 22. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013. PMID: 24151290 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Balasch J, Fabregues F, Creus M, Casamitjana R, Puerto B, Vanrell JA. Recombinant human follicle-stimulating hormone for ovulation induction in polycystic ovary syndrome: a prospective, randomised trial of two starting doses in a chronic low-dose step-up protocol. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2000;17:561–565. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Balen A, Platteau P, Nyboe Andersen A, Devroey P, Sørensen P, Helmgaard L, Arce J-C. The influence of body weight on response to ovulation induction with gonadotrophins in 335 women with World Health Organization group II anovulatory infertility. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 2006;113:1195–1202. - PubMed
-
- Balen A, Platteau P, Nyboe Andersen A, Devroey P, Helmgaard L, Arce J-C for the Bravelle Ovulation Induction (BOI) Study Group. Highly purified FSH is as efficacious as recombinant FSH for ovulation induction in women with WHO Group II anovulatory infertility: a randomized controlled non-inferiority trial. Hum Reprod. 2007;22:1816–1823. - PubMed
-
- Calaf Alsina J, Ruiz Balda JA, Romeu Sarrió A, Caballero Fernandez V, Cano Trigo I, Gómez Parga JL, González Batres C, Rodríguez Escudero FJ. Ovulation induction with a starting dose of 50IU of recombinant follicle stimulating hormone in WHO group anovulatory women: the IO-50 study, a prospective, observational, multicentre, open trial. Br Journal Obstet Gynaecol. 2003;110:1072–1077. - PubMed
-
- Chan CCW, Ng EHY, Chan MMY, Tang OS, Lau EYL, Yeung WSB, Ho PC. Bioavailability of hCG after intramuscular or subcutaneous injection in obese and non-obese women. Hum Reprod. 2003;18:2294–2297. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

