Inhibition of corneal inflammation by liposomal delivery of short-chain, C-6 ceramide
- PMID: 18372342
- PMCID: PMC3584160
- DOI: 10.1189/jlb.0108076
Inhibition of corneal inflammation by liposomal delivery of short-chain, C-6 ceramide
Abstract
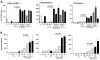
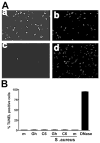
Ceramide is recognized as an antiproliferative and proapoptotic sphingolipid metabolite; however, the role of ceramide in inflammation is not well understood. To determine the role of C6-ceramide in regulating inflammatory responses, human corneal epithelial cells were treated with C6-ceramide in 80 nm diameter nanoliposome bilayer formulation (Lip-C6) prior to stimulation with UV-killed Staphylococcus aureus. Lip-C6 (5 muM) inhibited the phosphorylation of proinflammatory and proapoptotic MAP kinases JNK and p38 and production of neutrophil chemotactic cytokines CXCL1, CXCL5, and CXCL8. Lip-C6 also blocked CXC chemokine production by human and murine neutrophils. To determine the effect of Lip-C6 in vivo, a murine model of corneal inflammation was used in which LPS or S. aureus added to the abraded corneal surface induces neutrophil infiltration to the corneal stroma, resulting in increased corneal haze. Mice were treated topically with 2 nMoles (811 ng) Lip-C6 or with control liposomes prior to, or following, LPS or S. aureus stimulation. We found that corneal inflammation was significantly inhibited by Lip-C6 but not control liposomes given prior to, or following, activation by LPS or S. aureus. Furthermore, Lip-C6 did not induce apoptosis of corneal epithelial cells in vitro or in vivo, nor did it inhibit corneal wound healing. Together, these findings demonstrate a novel, anti-inflammatory, nontoxic, therapeutic role for liposomally delivered short-chain ceramide.
Figures


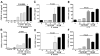




References
-
- Fuortes M, Jin W, Nathan C. Ceramide selectively inhibits early events in the response of human neutrophils to tumor necrosis factor. J Leukoc Biol. 1996;59:451–460. - PubMed
-
- Suchard SJ, Mansfield PJ, Boxer LA, Shayman JA. Mitogen-activated protein kinase activation during IgG-dependent phagocytosis in human neutrophils: inhibition by ceramide. J Immunol. 1997;158:4961–4967. - PubMed
-
- Nakamura T, Abe A, Balazovich KJ, Wu D, Suchard SJ, Boxer LA, Shayman JA. Ceramide regulates oxidant release in adherent human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:18384–18389. - PubMed
-
- Wong K, Li XB, Hunchuk N. N-acetylsphingosine (C2-ceramide) inhibited neutrophil superoxide formation and calcium influx. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:3056–3062. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

